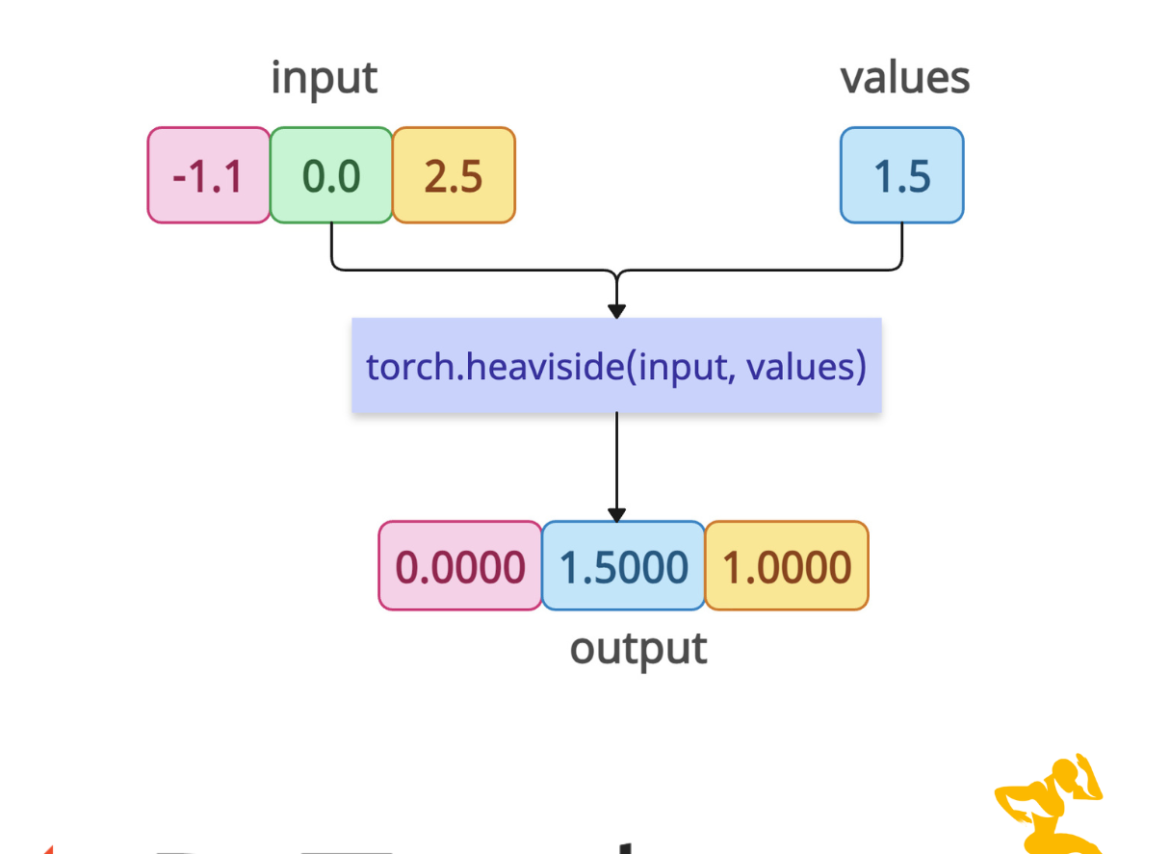
The torch.heaviside() method implements the Heaviside step function, a mathematical function that returns 0 for negative inputs, a specified value for zero inputs, and 1 for positive inputs.
Here is the summary for this method:
- If input < 0, the output is 0.
- If input > 0, the output is 1.
- If input == 0, the output is values (i.e., the corresponding element in the second tensor).
Syntax
torch.heaviside(input, values, out=None)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| input (Tensor) | It is an input tensor for the evaluation. |
| values (Tensor) | It is a tensor with multiple values or a scalar tensor that is returned when the input is zero. |
| out (Tensor, optional) | It is the output tensor to store the result (Default: None). |
Usage with scalar values
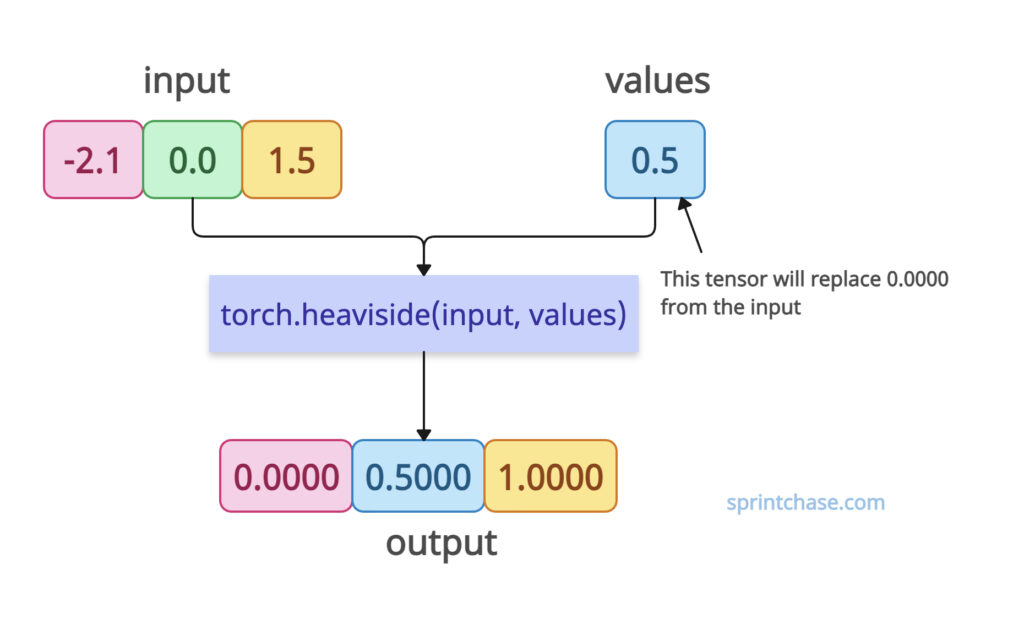
Let’s apply the Heaviside function to a tensor with a fixed value for zero inputs.
import torch input = torch.tensor([-2.1, 0.0, 1.5]) values = torch.tensor([0.5]) output = torch.heaviside(input, values) print(output) # Output: tensor([0.0000, 0.5000, 1.0000])
In this code, -2.1 becomes 0.0000, 0.0 becomes values tensor’s 0.5000, and 1.5 becomes 1.0000.
If you come across this RuntimeError: heaviside is not yet implemented for complex tensors, that means your input is a complex tensor.
Don’t use the complex tensor because the .heaviside() method does not support complex tensors as of PyTorch 2.7.
The primary applications of the Heaviside function include signal processing, physics modeling, and custom autograd logic.
2D tensor
When it comes to a 2D tensor, the values of the tensor are applied column-wise. When broadcasting occurs, each column gets assigned its corresponding value from the values tensor.
import torch
input_2d = torch.tensor([[-2.1, 0.0, 1.5],
[0.0, -5.1, 0.0]])
values = torch.tensor([0.5, 0.6, 0.7])
output = torch.heaviside(input_2d, values)
print(output)
# Output:
# tensor([[0.0000, 0.6000, 1.0000],
# [0.5000, 0.0000, 0.7000]])
Here, in the first column, there are two values: -2.1 and 0.0.
Now, negative values will be replaced with 0.0, and the corresponding value from the values tensor will replace 0.0. Since this is the first column, the first element of the values tensor will replace it. So, 0.0 will be replaced by 0.5.
In the second column, 0.0 is replaced by the second value of the values tensor, which is 0.6, and a negative value is replaced with 0.0. The same logic is applied to the third column as well.
Let’s consider a slightly complex 2D tensor where we don’t include any 0.0 values in the first column of the input tensor.
import torch
input_2d = torch.tensor([[-2.1, 0.0, 1.5],
[3.0, -5.1, 0.0]])
values = torch.tensor([0.5, 0.6, 0.7])
output = torch.heaviside(input_2d, values)
print(output)
# Output:
# tensor([[0.0000, 0.6000, 1.0000],
# [1.0000, 0.0000, 0.7000]])
In this code, the values tensor is broadcast to match the shape of input_2d, so each zero in the input gets replaced by the corresponding value from the values tensor.
That means, in the first column, there is no zero, so the values tensor’s first value won’t be replaced.
Now, in the second column, there is 0.0, and the corresponding value in the values tensor is 0.6, so 0.6 will be included in the output.
The same logic applies in the third column, and 0.7 is included in the output.
“Values” tensor is empty
What if the values tensor is empty? That means we don’t have any value to replace 0. Let’s find out.
import torch
input = torch.tensor([-2.1, 0.0, 1.5])
empty_values = torch.tensor([])
output = torch.heaviside(input, empty_values)
print(output)
# RuntimeError: The size of tensor a (3) must match the size of tensor b (0) at non-singleton dimension 0
And we get a RuntimeError. That means it is necessary to have at least one element in the Values tensor.
Broadcasting error
If you have a 1D PyTorch tensor with more 0.0 values than elements in the values tensor, PyTorch will raise a broadcasting error like this: RuntimeError: The size of tensor a (6) must match the size of tensor b (3) at non-singleton dimension 0
import torch # 1D input with 5 elements, including multiple zeros input_1d = torch.tensor([-1.0, 0.0, 2.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]) # Values tensor with only 3 elements values = torch.tensor([0.5, 0.6, 0.7]) output_tensor = torch.heaviside(input_1d, values) # Output: # RuntimeError: The size of tensor a (6) must match the size of tensor b (3) at non-singleton dimension 0
To fix this type of error, ensure that the input and value tensors have compatible shapes.