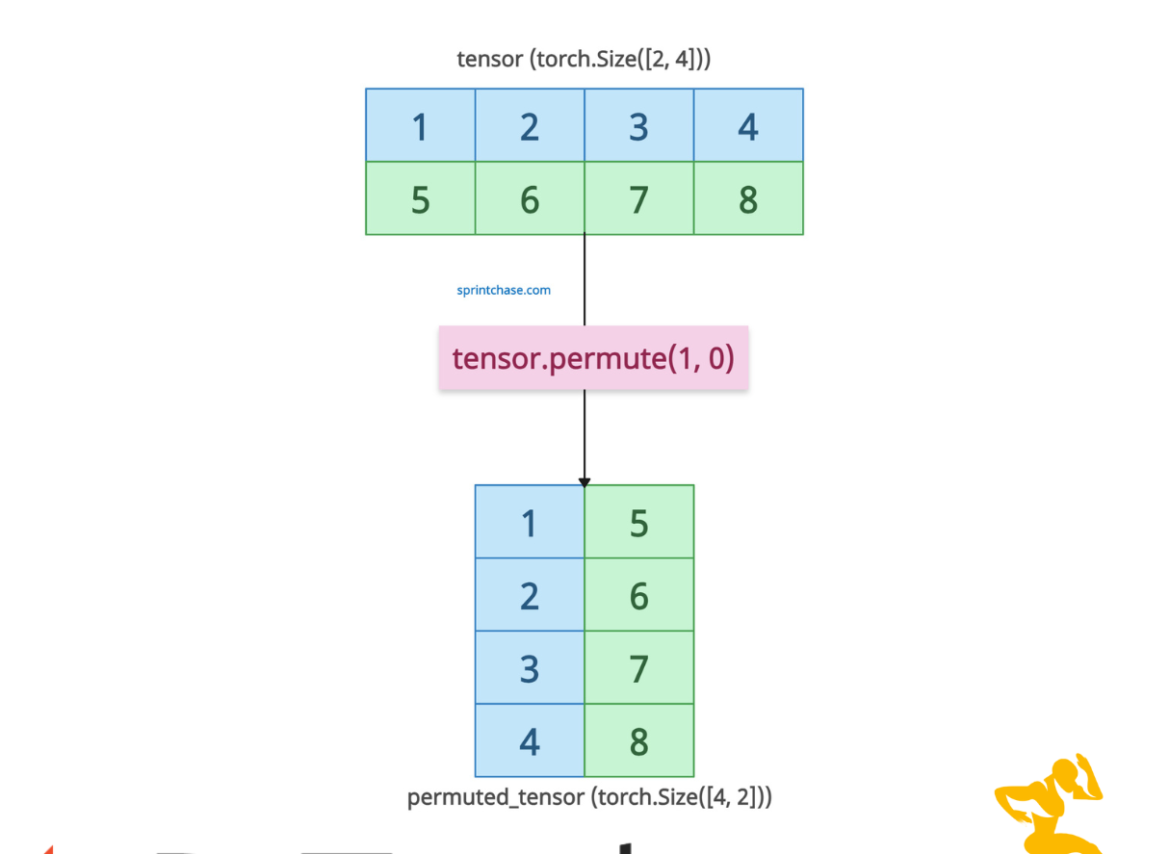
The torch.permute() method reorders the dimensions of a tensor based on a specified permutation. The output tensor is a view (not a copy) of the original tensor with its dimensions permuted; the original tensor remains unchanged.
The output tensor shares the data with the input tensor, and that is why changes to the permuted tensor affect the original.
Unlike torch.transpose() method, which swaps only two dimensions, torch.permute() method allows for arbitrary reordering of all dimensions, offering greater flexibility.
A great example of this method is when working with convolutional layers or batch processing, where you need to reshape your tensor for matrix operations.
Syntax
torch.permute(input, dims) # or tensor.permute(*dims)
Most of the time, we will use the syntax: tensor.permute() because we will have a tensor and we will just operate on it.
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| input (Tensor) | It represents an input tensor that requires permutation. |
| dims (tuple of ints) | It is the desired ordering of the dimensions.
It must contain all dimension indices (0 to input.dim() – 1) exactly once. |
Basic Permutation with 2D Tensor
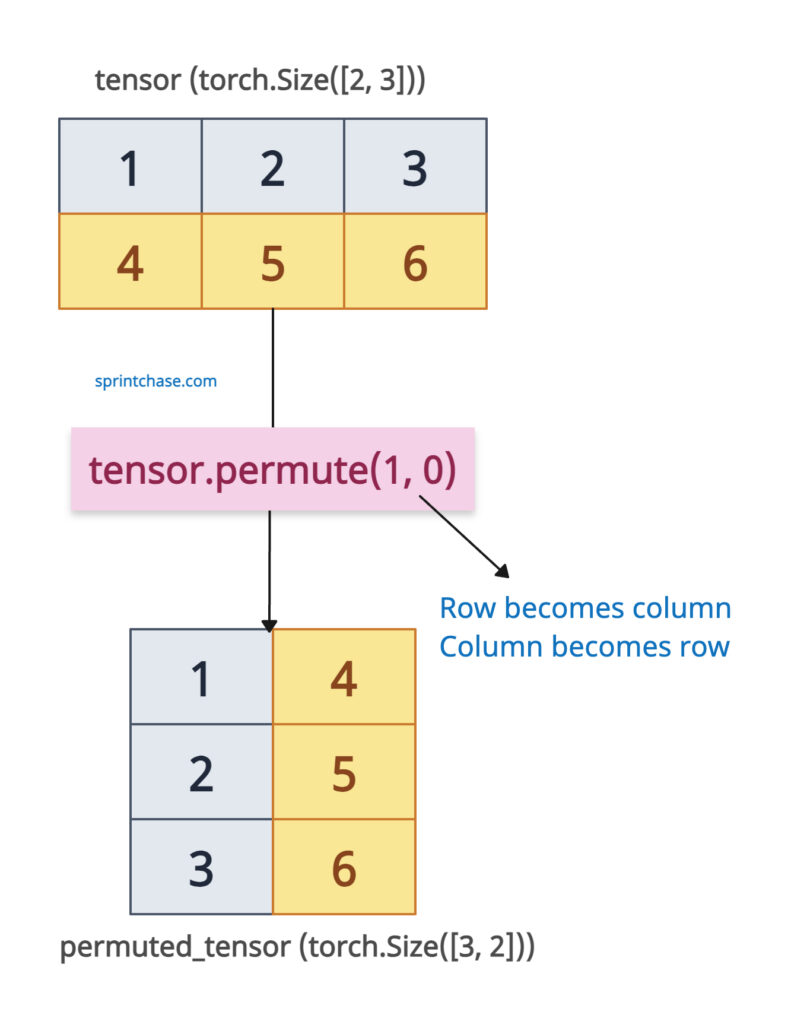
Let’s transpose a matrix (2D Tensor) that has shape (2, 3):
import torch
tensor = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])
print(tensor)
# Output:
# tensor([[1, 2, 3],
# [4, 5, 6]])
print(tensor.shape)
# Output: torch.Size([2, 3])
permuted_tensor = tensor.permute(1, 0)
print(permuted_tensor)
# Output:
# tensor([[1, 4],
# [2, 5],
# [3, 6]])
print(permuted_tensor.shape)
# Output: torch.Size([3, 2])
print(permuted_tensor.is_conj())
# Output: False
The input tensor has a shape (2, 3), and after rearranging the dimensions, the output tensor has a shape (3, 2), making the columns (dim 1) the new rows (dim 0).
How does this happen? When we call a tensor.permute(1, 0), we are basically saying, take dimension 1 of the original tensor and make it the new dimension 0, and take dimension 0 and make it the new dimension 1.
Reordering 3D Tensor
For batch processing in neural networks, we may need to reorder a 3D tensor.
import torch tensor = torch.randn(2, 3, 5) print(tensor.shape) # Output: (2, 3, 5) permuted = tensor.permute(2, 0, 1) print(permuted.shape) # Output: (5, 2, 3)
Invalid dimension indices
If we repeat indices while reordering, it will throw a RuntimeError: permute(): duplicate dims are not allowed.
import torch tensor = torch.randn(2, 3, 4) permuted = tensor.permute(0, 0, 2) # Output: RuntimeError: permute(): duplicate dims are not allowed.
The dims tuple must contain each dimension index exactly once. If they appear more than once, it will throw this type of error.
Non-contiguous tensor handling
After using the .permute() method, the output tensor can be non-contiguous. To make it contiguous, we can use the .contiguous() method on that tensor.
import torch tensor = torch.randn(3, 4, 5) permuted = tensor.permute(2, 1, 0) print(permuted.is_contiguous()) # Output: False contiguous = permuted.contiguous() print(contiguous.is_contiguous()) # Output: True
That’s all!