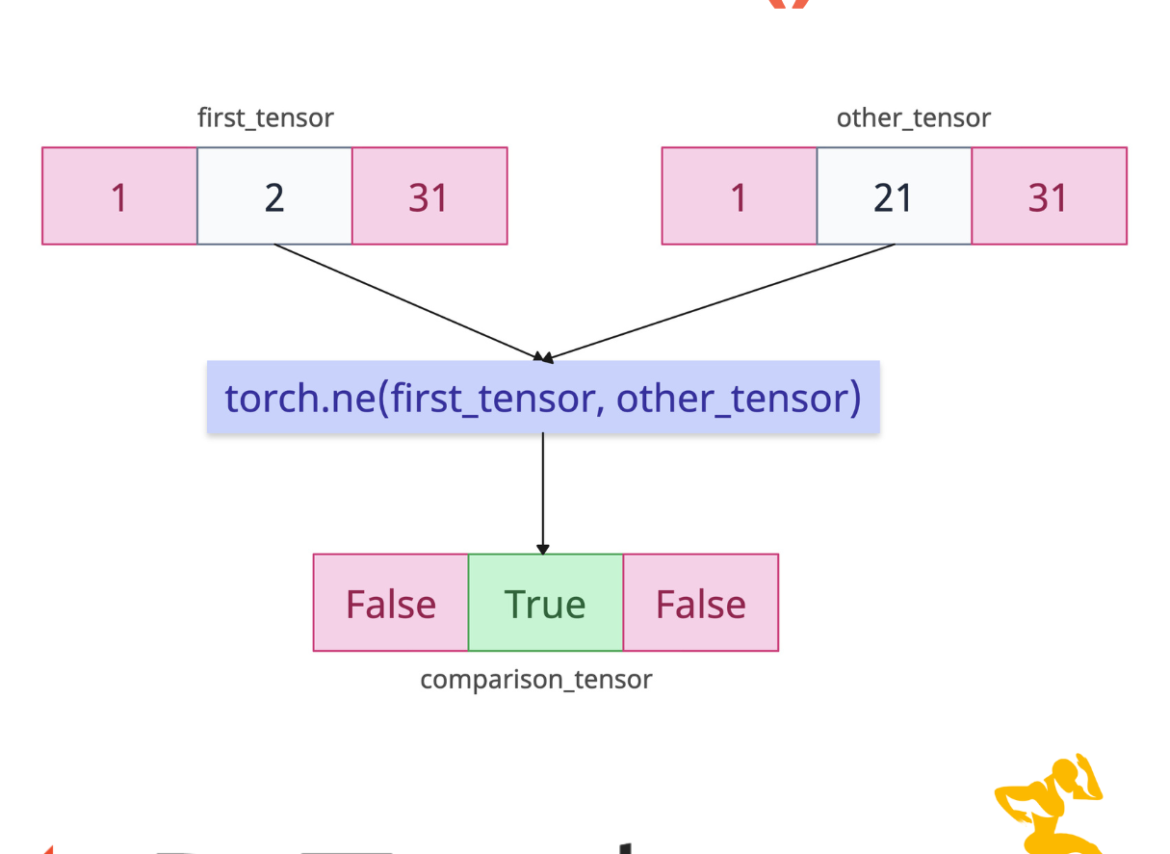
The torch.ne() method performs an element-wise comparison between two tensors, returning a boolean tensor where each element is True if the corresponding elements in the input tensors are not equal, and False otherwise.
It basically does a “not equal” comparison between two tensors.
The second argument can be a number or a tensor whose shape is broadcastable with the first argument.
Syntax
torch.ne(input, other, out=None)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| input (Tensor) | It represents the first tensor. |
| other (Tensor or Scalar) | It represents the second input tensor or a scalar to compare. |
| out (Tensor, optional) |
It represents the output tensor to store the result. |
Element-wise comparison of tensor elements
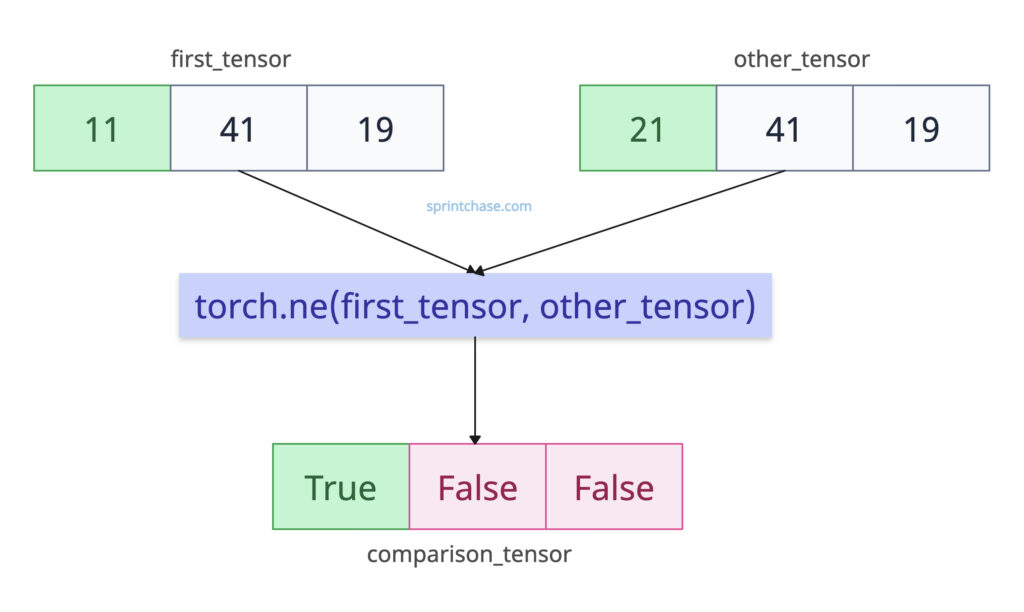
Let’s define two tensors with the same shape and size and see how many elements from both are not equal.
import torch first_tensor = torch.tensor([11, 41, 19]) other_tensor = torch.tensor([21, 41, 19]) comparison_tensor = torch.ne(first_tensor, other_tensor) print(comparison_tensor) # Output: tensor([ True, False, False])
The above output shows the output result is True where elements differ (11 != 21). Others are the same, so it returned False where they are equal (41 == 41, 19 == 19).
Scalar comparison
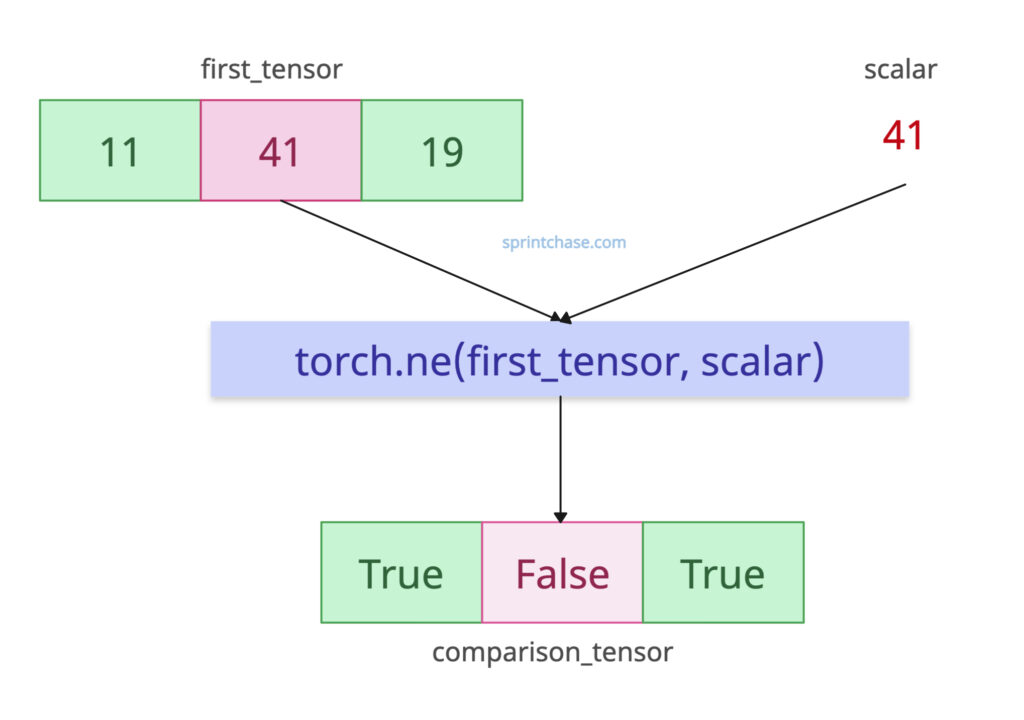 Let’s compare a tensor with a scalar value.
Let’s compare a tensor with a scalar value.
import torch first_tensor = torch.tensor([11, 41, 19]) scalar = 41 comparison_tensor = torch.ne(first_tensor, scalar) print(comparison_tensor) # Output: tensor([ True, False, True])
In this code, the scalar 41 is broadcast to match the shape of first_tensor, resulting in True where elements are not equal to 41.
Empty tensors
If the input tensors are empty, the output of this method will be an empty boolean tensor too, since there is nothing to compare.
import torch empty_t1 = torch.tensor([]) empty_t2 = torch.tensor([]) result = torch.ne(empty_t1, empty_t2) print(result) # Output: tensor([])
Incompatible shapes
What if the first_tensor and other_tensor have incompatible shapes? Well, it throws RuntimeError and crashes the program. But we can handle it using a try-except block.
import torch
a = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
b = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])
try:
result = torch.ne(a, b)
except RuntimeError as e:
print(e)
# Output: The size of tensor a (2) must match the size of tensor
# b (3) at non-singleton dimension 1
That’s all!