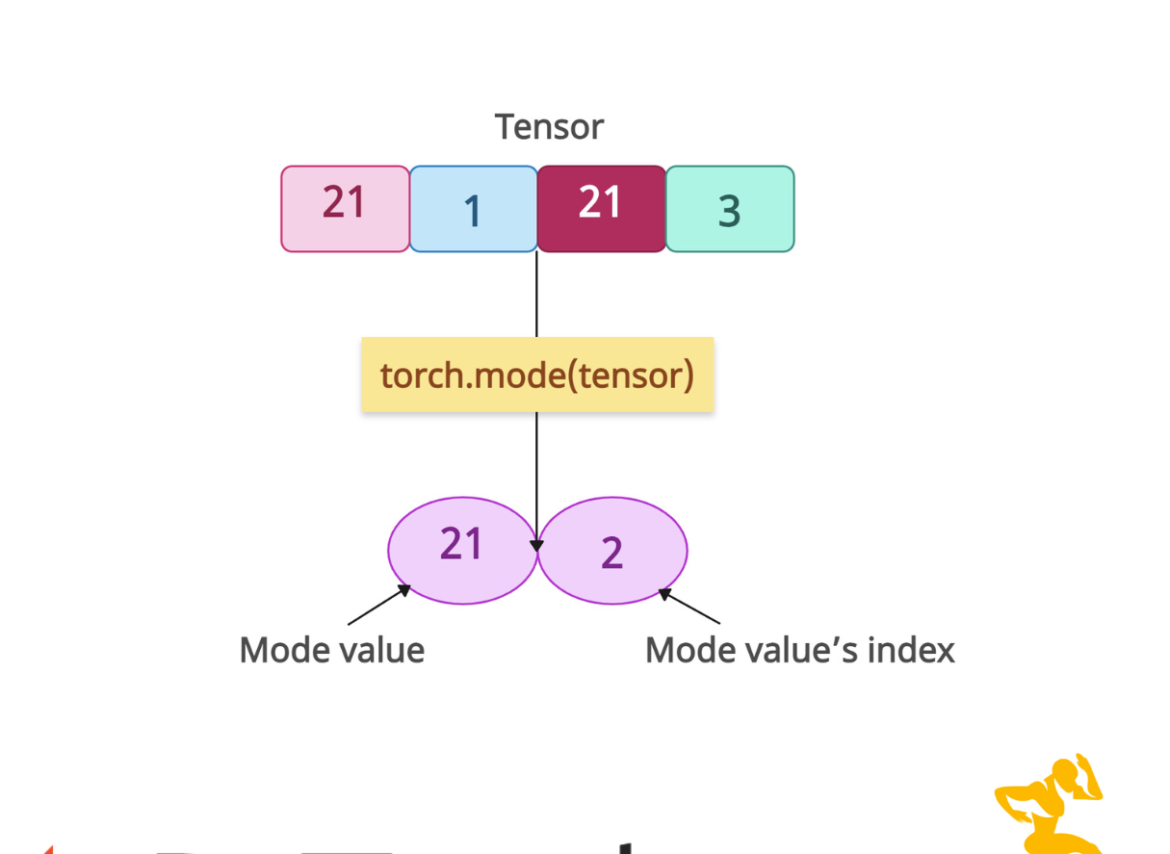
The torch.mode() method calculates the mode (i.e., the most frequent value) along a specified dimension of a tensor. It returns a namedtuple (values, indices) where:
- values: Mode values (most frequent elements).
- indices: Positions of the first occurrence of the mode in the input dimension.
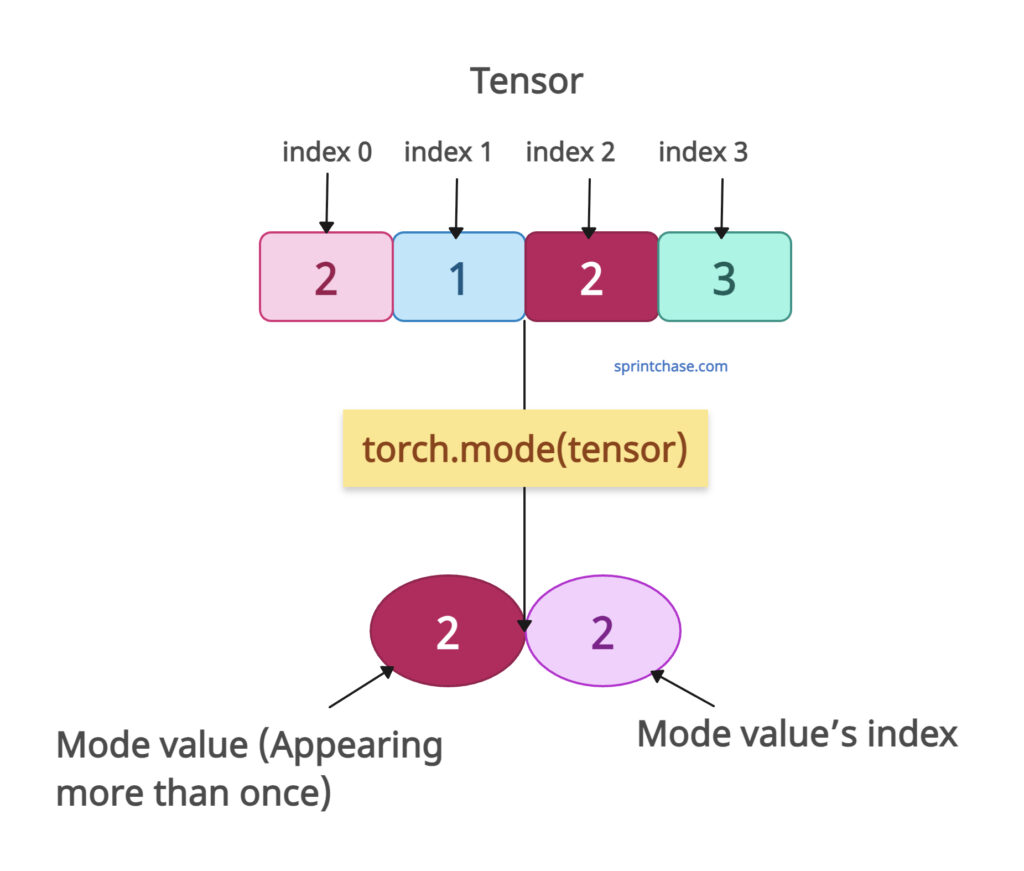
For example, if I have a tensor(2, 1, 2, 3), the mode of this tensor is 2 because it appears more than once.
Syntax
torch.mode(
input,
dim = -1,
keepdim = False,
out = None
)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| input (Tensor) | It represents an input tensor. |
| dim (int) |
It is the dimension along which the mode is calculated. By default, the last dimension is -1. |
| keepdim (bool, optional) |
If True, it retains the reduced dimension as size 1 in the output. The default is False. |
| out (tuple (Tensor, Tensor), optional) | It is an output tuple for results. |
Calculating Mode along the default dimension (Last Dimension)
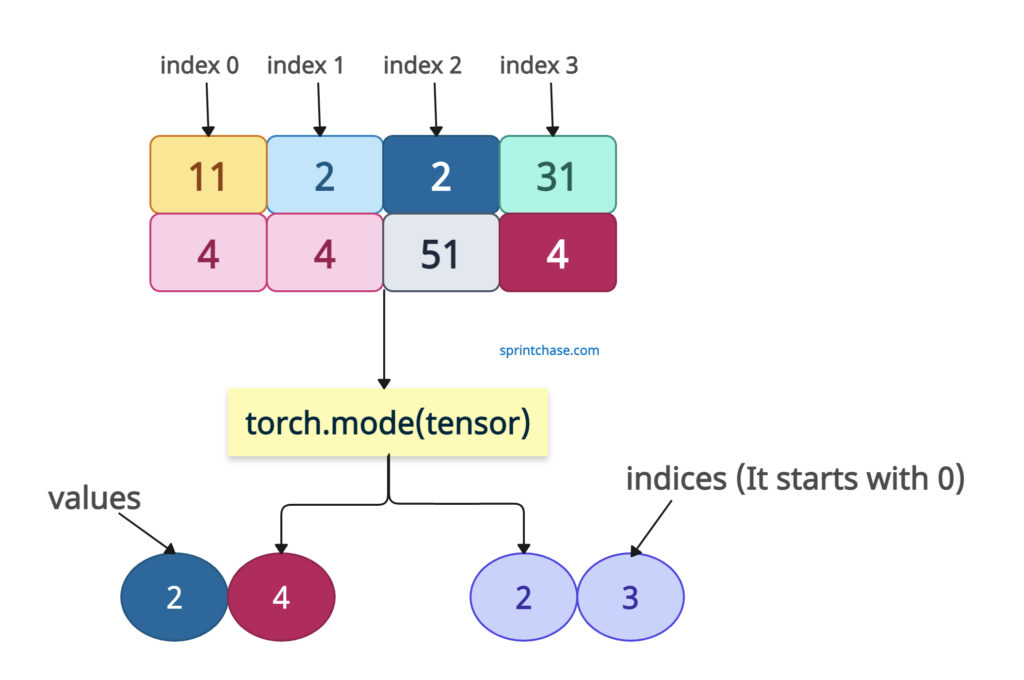
For a 2D tensor, calculate the mode along the last dimension (i.e., the columns).
import torch
tensor = torch.tensor([[11, 2, 2, 31],
[4, 4, 51, 4]])
mode = torch.mode(tensor)
print(mode)
# Output:
# torch.return_types.mode(
# values=tensor([2, 4]),
# indices=tensor([2, 3]))
Let me explain the output:
- For the first row [1, 2, 2, 3], the mode is 2 (appears twice) at index 2.
- For the second row [4, 4, 5, 4], the mode is 4 (appears three times) at index 1.
Specifying a dimension
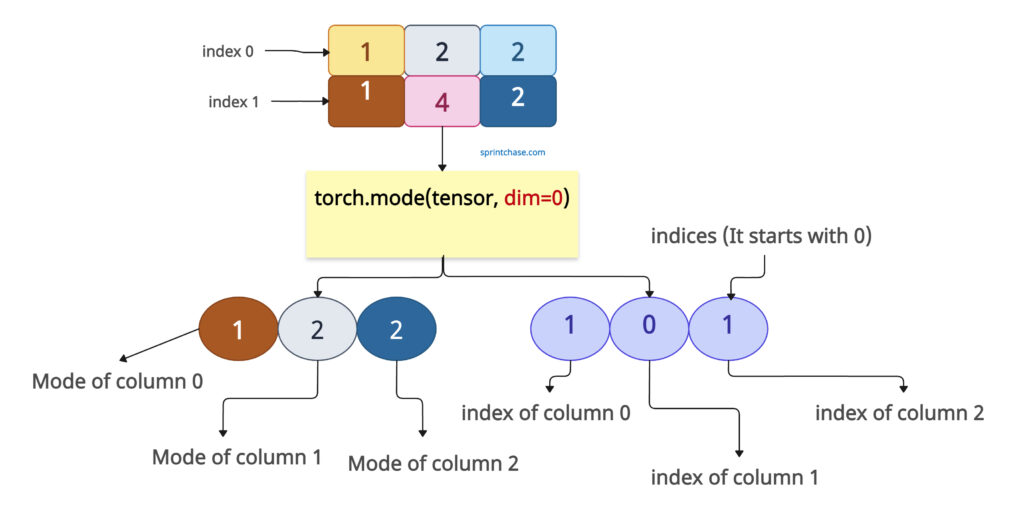
We can calculate the mode along the first dimension (rows).
import torch
tensor = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 2],
[1, 4, 2]])
mode_at_row = torch.mode(tensor, dim=0)
print(mode_at_row)
# Output:
# torch.return_types.mode(
# values=tensor([1, 2, 2]),
# indices=tensor([1, 0, 1]))
For the first column [1, 1], the mode is 1 at index 1.
For the second column [2, 4], the mode is 2 (the smallest value if tied) at index 0.
For the third column [2, 2], the mode is 2 at index 1.
Using keepdim=True
You can retain the reduced dimension as size 1.
import torch
tensor = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 2],
[1, 4, 2]])
result = torch.mode(tensor, dim=0, keepdim=True)
print(result)
# Output:
# torch.return_types.mode(
# values=tensor([[1, 2, 2]]),
# indices=tensor([[1, 0, 1]]))
From the above code, you can see that the output tensors have a shape of [1, 3] instead of [3], due to the keepdim=True parameter, which preserves the dimension for further operations.
Handling ties
What if you have multiple values that have the same frequency? In that case, the smallest value is selected.
import torch tensor = torch.tensor([1, 1, 2, 2, 3]) result = torch.mode(tensor) print(result) # Output: # torch.return_types.mode( # values=tensor(1), # indices=tensor(1))
In the above code, values 1 and 2 both appear twice, but only value 1 is selected because it is smaller at an index of 0.