The torch.manual_seed() method sets the seed for the random number generator used by PyTorch’s random operations on the CPU and CUDA devices (if applicable).
It returns the torch.Generator object can be used with other PyTorch functions (e.g., DataLoader) to control randomness.
It affects random functions like weight initialization, data shuffling, or random sampling.
Syntax
torch.manual_seed(seed)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| seed (int) | It represents the desired seed value for the random number generator. It should not be a negative value. Integer value’s range must be (0 ≤ seed ≤ 2^32 – 1) to initialize the RNG. |
Reproducible random tensor
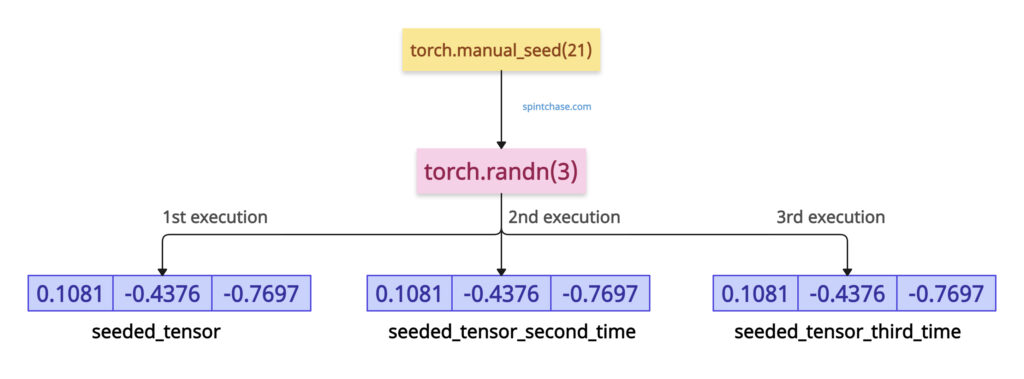
You can set the seed to generate the same random tensor every time, which is the basic working of this method. For generating a random number, you can use torch.randn() method.
import torch torch.manual_seed(21) seeded_tensor = torch.randn(3) print(seeded_tensor) # Output: tensor([ 0.1081, -0.4376, -0.7697]) torch.manual_seed(21) # Reset seed seeded_tensor_second_time = torch.randn(3) print(seeded_tensor_second_time) # Output: tensor([ 0.1081, -0.4376, -0.7697])
In the above code, we set the seed to 21. Setting it will generate the same tensor each time you execute the program.
Consistent neural network weights
If you are working with neural networks, you must initialize consistent weights across all the runs. For that, the manual_seed() method is helpful.
import torch import torch.nn as nn torch.manual_seed(123) model1 = nn.Linear(4, 2) print(model1.weight) # Output: # Parameter containing: # tensor([[-0.2039, 0.0166, -0.2483, 0.1886], # [-0.4260, 0.3665, -0.3634, -0.3975]], requires_grad=True) torch.manual_seed(123) model2 = nn.Linear(4, 2) print(model2.weight) # Output: # Parameter containing: # tensor([[-0.2039, 0.0166, -0.2483, 0.1886], # [-0.4260, 0.3665, -0.3634, -0.3975]], requires_grad=True) # Executing second time # Output: # Parameter containing: # tensor([[-0.2039, 0.0166, -0.2483, 0.1886], # [-0.4260, 0.3665, -0.3634, -0.3975]], requires_grad=True)
The above code shows that the seed ensures the initialization of random weights in the nn.Linear is identical across all model instances, which can be helpful in debugging.
We have executed the above code twice, giving the same weights each time.
Data shuffling
You can use this method to control the shuffling order in DataLoader.import torch
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
data = torch.arange(6)
dataset = TensorDataset(data)
torch.manual_seed(42)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True)
for batch in dataloader:
# Consistent order, e.g., tensor([4, 1]), tensor([3, 5]), tensor([0, 2])
print(batch[0])
# Output:
# tensor([4, 5])
# tensor([1, 0])
# tensor([3, 2])
# Executing Second Time
# Output:
# tensor([4, 5])
# tensor([1, 0])
# tensor([3, 2])
Using torch.manual_seed(42), we ensured the DataLoader shuffles the data in the same order each run, making the batch sequence predictable and reproducible.