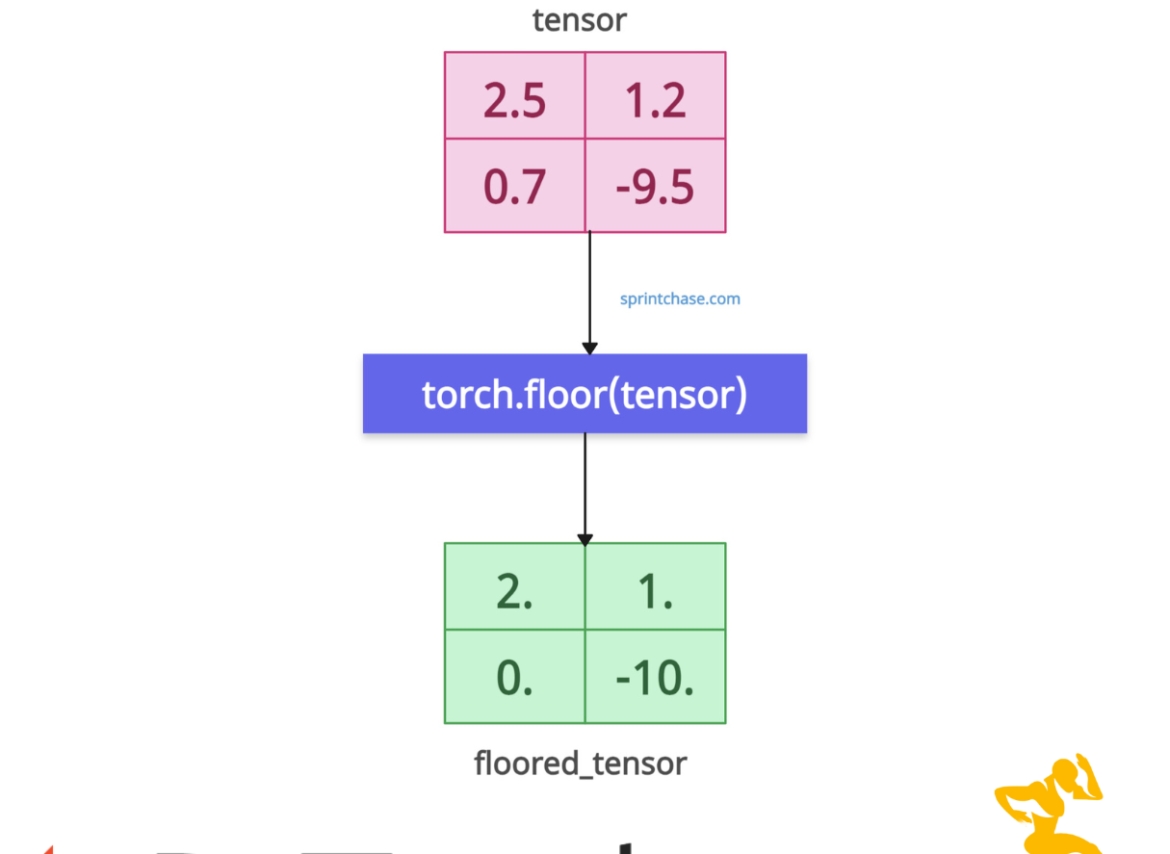
The torch.floor() method returns the largest integer less than or equal to each element of the input tensor, effectively rounding down to the nearest integer. For example, 1.8 becomes 1, 0.8 becomes 0, and -2.1 becomes -3.
 The basic formula is this: outi=⌊inputi⌋
The basic formula is this: outi=⌊inputi⌋
It preserves the input tensor’s shape and data type and performs element-wise operations.
The torch.ceil() method does exactly the opposite. It returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to each input element of the tensor.
Function signature
torch.floor(input, out=None)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| input (Tensor) |
It represents an input tensor whose elements need to be floored. It can be of any numeric data type. For example, float32, float64, or int32. |
| out (Tensor, optional) | By default, its value is None, but you can use this argument to store the floor results into a pre-allocated tensor. |
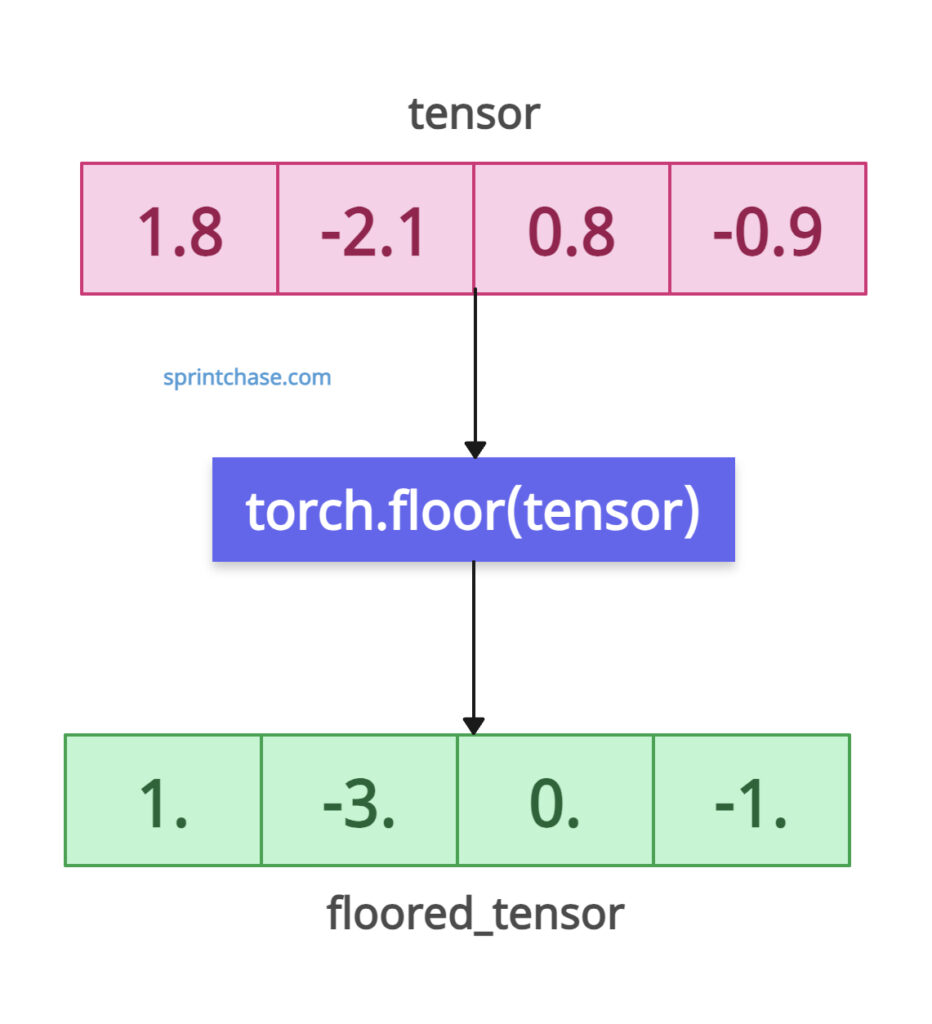
Element-wise flooring of a 1D tensor
Let’s round down a floating-point value in a tensor.
import torch tensor = torch.tensor([1.8, -2.1, 0.8, -0.9]) floored_tensor = torch.floor(tensor) print(floored_tensor) # Output: tensor([ 1., -3., 0., -1.])
In the above code, the first element is 1.8, and the floored value is 1. That means it was rounded down to the nearest integer. The output element 1 is less than 1.8 and the nearest integer.
In the case of negative values, -2.1 is greater than -3. That’s why -3 is returned because it returns less than the input value. Our input value is -2.1; the returning value should be less than this.
If you apply the same logic to all the values, you will understand the whole output.
Multi-dimensional Tensors
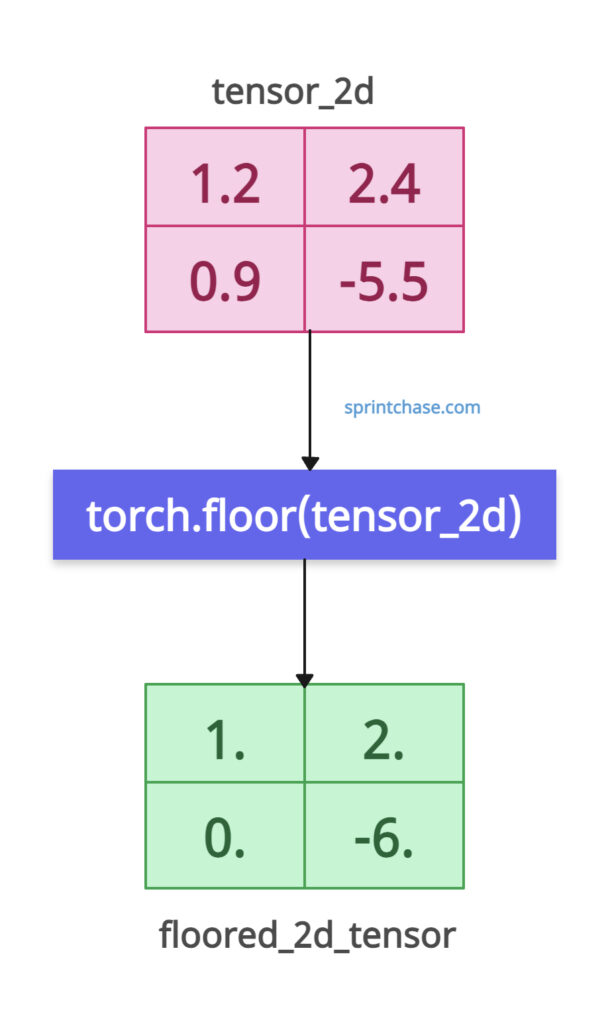
What if our input is a multidimensional tensor, like a 2D (Matrix) or 3D tensor? Well, it works the same in a 2D tensor. It returns the same shape and size tensor with floored values in the output.
import torch
tensor_2d = torch.tensor([[1.2, 2.4],
[0.9, -5.5]])
floored_2d_tensor = torch.floor(tensor_2d)
print(floored_2d_tensor)
# Output: tensor([[1., 2.],
# [0., -6.]])
The above output shows that it is a 2D tensor, and each value of the input tensor is floored individually.
Pre-allocated tensor
You can create a tensor that will act as pre-allocated using torch.empty() method, and then you can save the floor-valued tensor into this tensor using the “out” argument.
import torch tensor_1d = torch.tensor([1.5, -2.9, 0.4]) pre_alloc_tensor = torch.empty(3) torch.floor(tensor_1d, out=pre_alloc_tensor) print(pre_alloc_tensor) # Output: tensor([ 1., -3., 0.])
Integer tensor
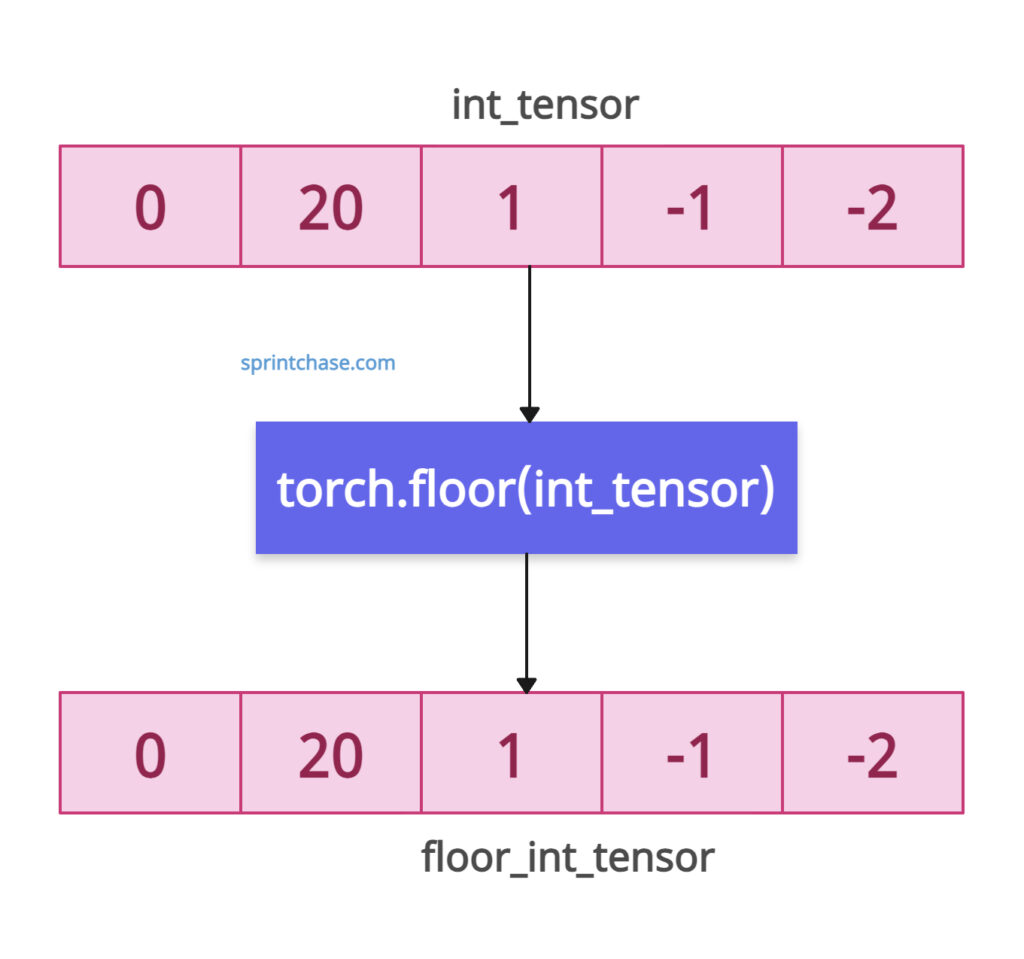
What if our input tensor has integer values? Well, it will remain as it is and will not get floored because floating values are eligible for flooring.
import torch int_tensor = torch.tensor([0, 20, 1, -1, -2], dtype=torch.int32) floor_int_tensor = torch.floor(int_tensor) print(floor_int_tensor) # Output: tensor([ 0, 20, 1, -1, -2], dtype=torch.int32)
In-place modification
To modify in-place in the original input tensor, we can use the tensor.floor_() method. It works the same as a torch.floor() method.
import torch input_tensor = torch.tensor([1.1, 2.1, -1.9]) input_tensor.floor_() print(input_tensor) # Output: tensor([ 1., 2., -2.])
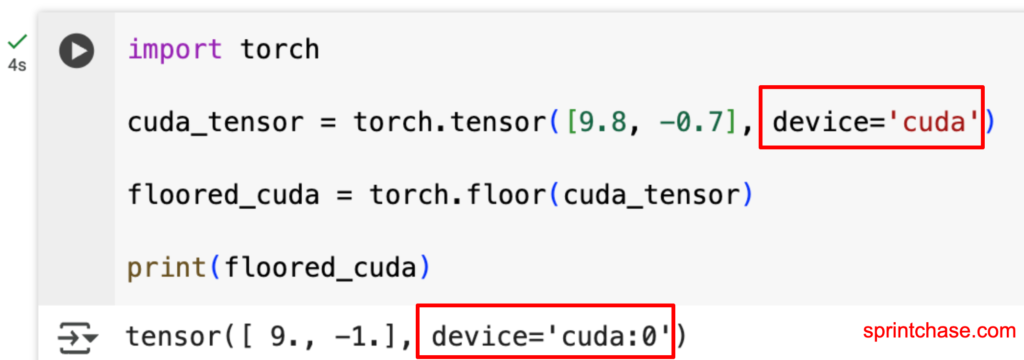
CUDA Tensor Support
If you want to perform flooring on an NVIDIA CUDA GPU, you can do that without hassle.import torch cuda_tensor = torch.tensor([9.8, -0.7], device='cuda') floored_cuda = torch.floor(cuda_tensor) print(floored_cuda)
 That’s all!
That’s all!