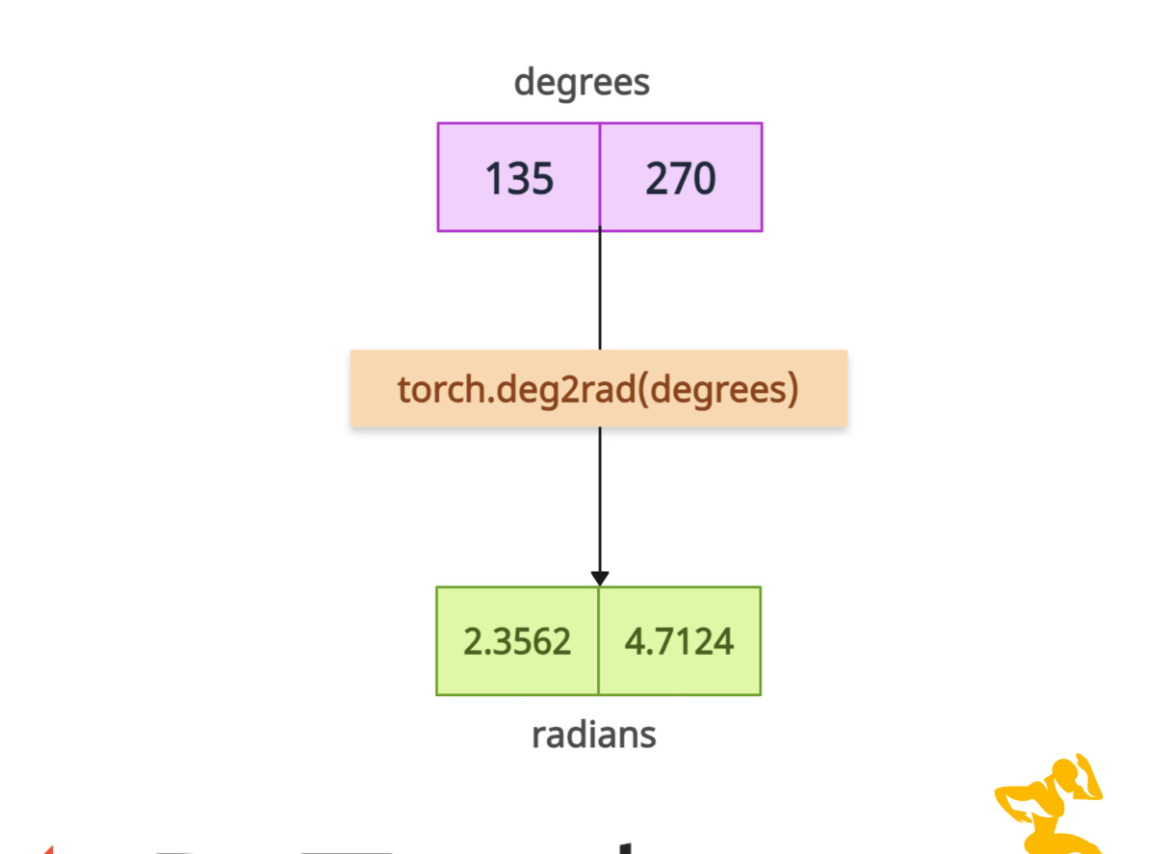
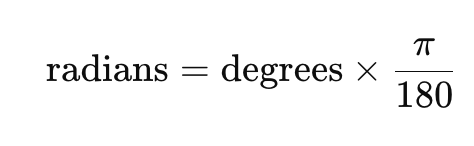PyTorch torch.deg2rad() method converts angles from degrees to radians.
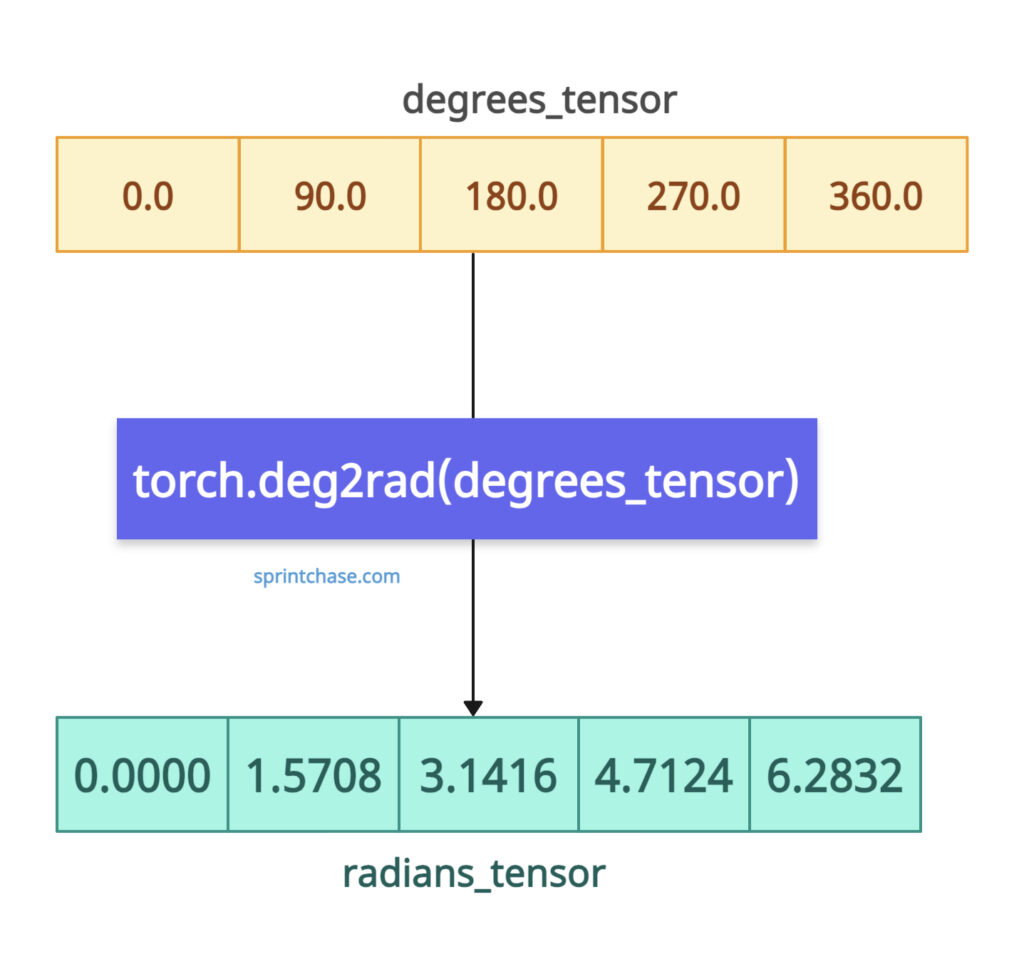
It returns a tensor of the same shape and data type as the input, containing angles converted to radians.
The mathematical formula is this:
Syntax
torch.deg2rad(input, out=None)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| input (Tensor) | It represents a tensor containing angle values in degrees. |
| out (Tensor, optional) | It represents a tensor to store the output. |
Basic conversion
import torch
degrees_tensor = torch.tensor([0.0, 90.0, 180.0, 270.0, 360.0])
print("Degrees Tensor:", degrees_tensor)
# Output: Degrees Tensor: tensor([ 0., 90., 180., 270., 360.])
radians_tensor = torch.deg2rad(degrees_tensor)
print("Radians Tensor:", radians_tensor)
# Output: Radians Tensor: tensor([0.0000, 1.5708, 3.1416, 4.7124, 6.2832])
You can see from the above output that it converted element-wise and returns the same shape sensor with radian values.
Negative angles
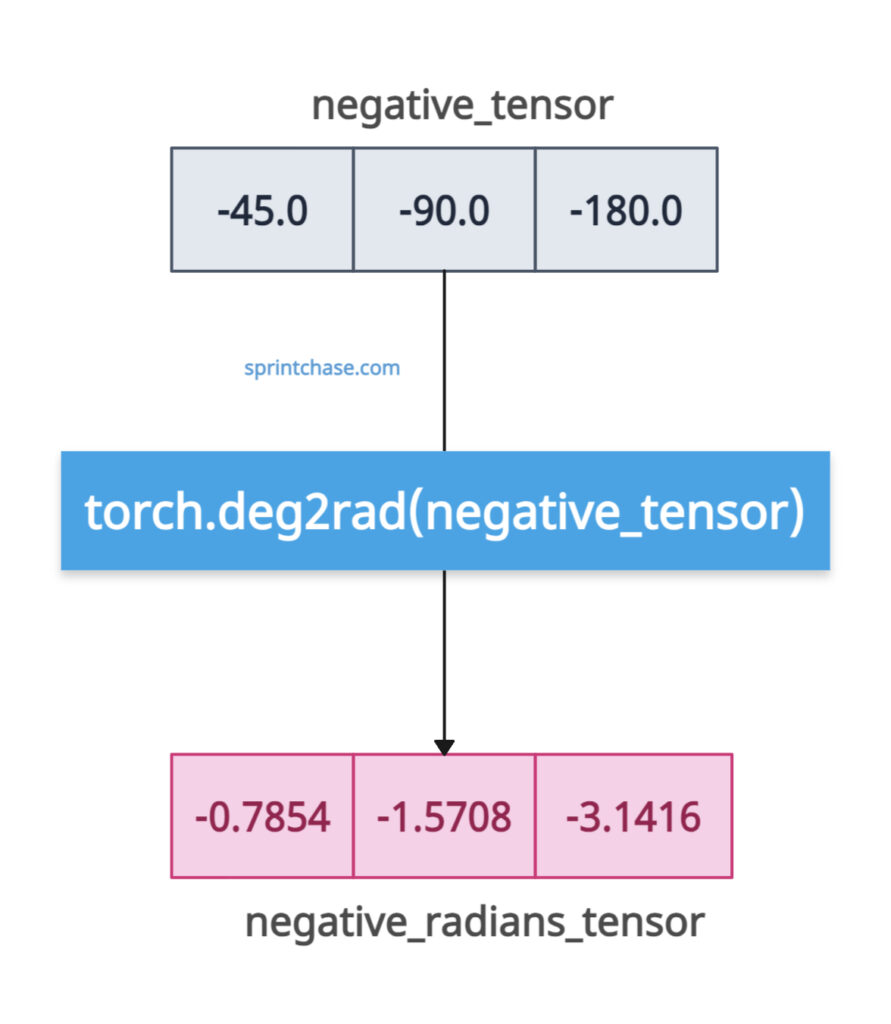 If you pass a tensor with negative degrees, it will give you the negative radians.
If you pass a tensor with negative degrees, it will give you the negative radians.
import torch
negative_tensor = torch.tensor([-45.0, -90.0, -180.0])
print("Negative Degrees Tensor:", negative_tensor)
# Output: Negative Degrees Tensor: tensor([-45., -90., -180.])
negative_radians_tensor = torch.deg2rad(negative_tensor)
print("Negative Radians Tensor:", negative_radians_tensor)
# Output: Negative Radians Tensor: tensor([-0.7854, -1.5708, -3.1416])
Handling a 2D tensor of degrees
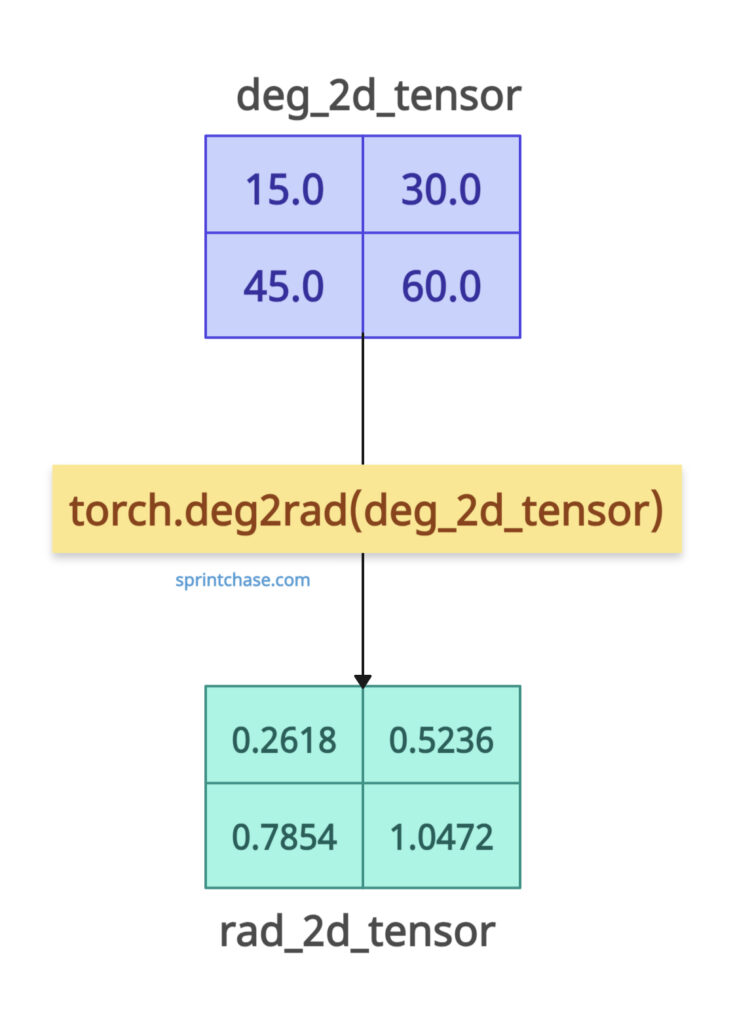
If you pass the degrees in a 2D tensor, it will return radians in a 2D tensor. Dimensions do not matter. It works smoothly.
import torch
deg_2d_tensor = torch.tensor([[15.0, 30.0], [45.0, 60.0]])
print("2D Degrees Tensor:", deg_2d_tensor)
# Output: 2D Degrees Tensor: tensor([[15., 30.],
# [45., 60.]])
rad_2d_tensor = torch.deg2rad(deg_2d_tensor)
print("2D Radians Tensor:", rad_2d_tensor)
# Output: 2D Radians Tensor: tensor([[0.2618, 0.5236],
# [0.7854, 1.0472]])
Pre-allocated tensor
If you have a pre-allocated tensor created using methods like torch.empty(), you can store the radian values in this tensor.
import torch input_tensor = torch.tensor([45.0, 135.0]) print(input_tensor) # Output: tensor([ 45., 135.]) output_tensor = torch.empty(2) print(output_tensor) # Output: tensor([0., 0.]) torch.deg2rad(input_tensor, out=output_tensor) print(output_tensor) # Output: tensor([0.7854, 2.3562])
Integrate with Trigonometric Functions
Let’s calculate the sine of 30 degrees.import torch
degrees = torch.tensor(30.0)
radians = torch.deg2rad(degrees)
sine = torch.sin(radians)
print(f"Sine of {degrees.item()} degrees is {sine.item()}")
# Output: Sine of 30.0 degrees is 0.5
That’s all!