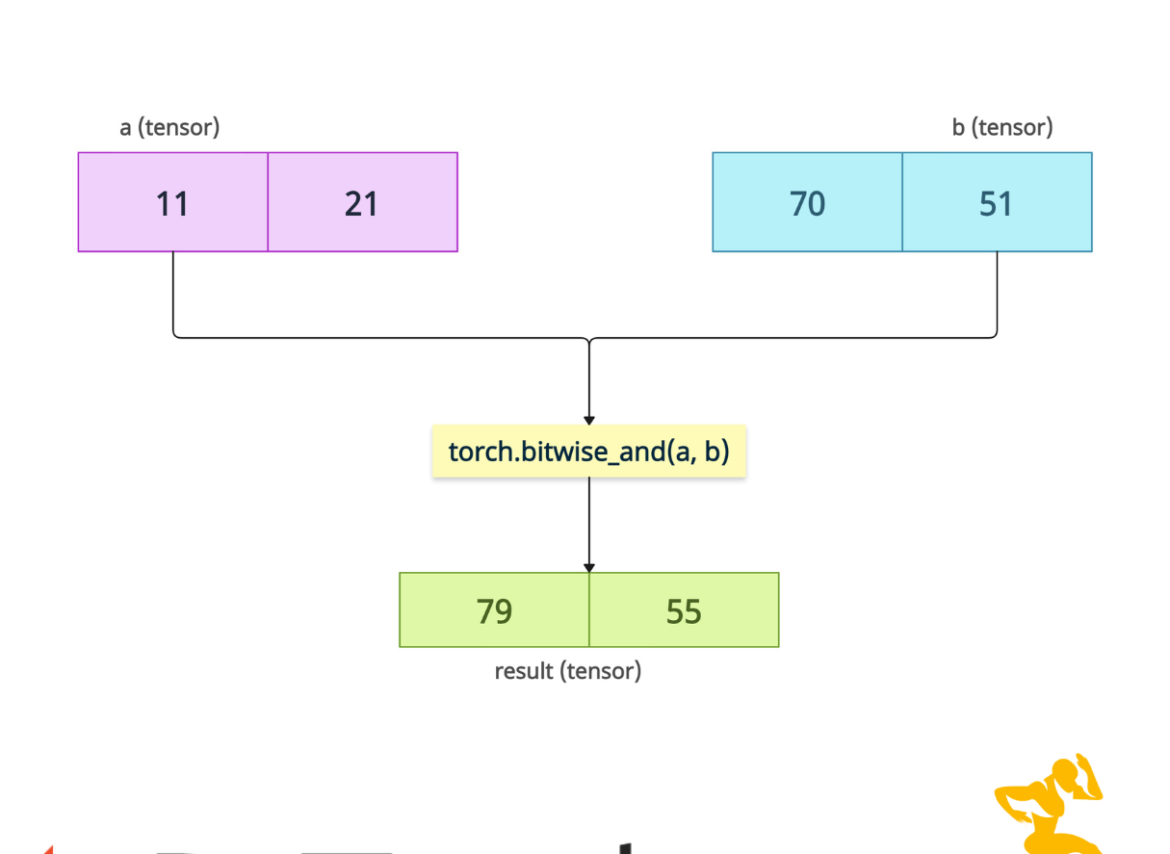
The torch.bitwise_and() method performs a bitwise AND operation on the binary representations of the integer values in the tensors. It supports both tensor-tensor operations and tensor-scalar operations.
Before we proceed, we need to understand how the bitwise AND works with 1 and 0.Bitwise AND Truth Table
| Input A | Input B | A & B (Output) |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
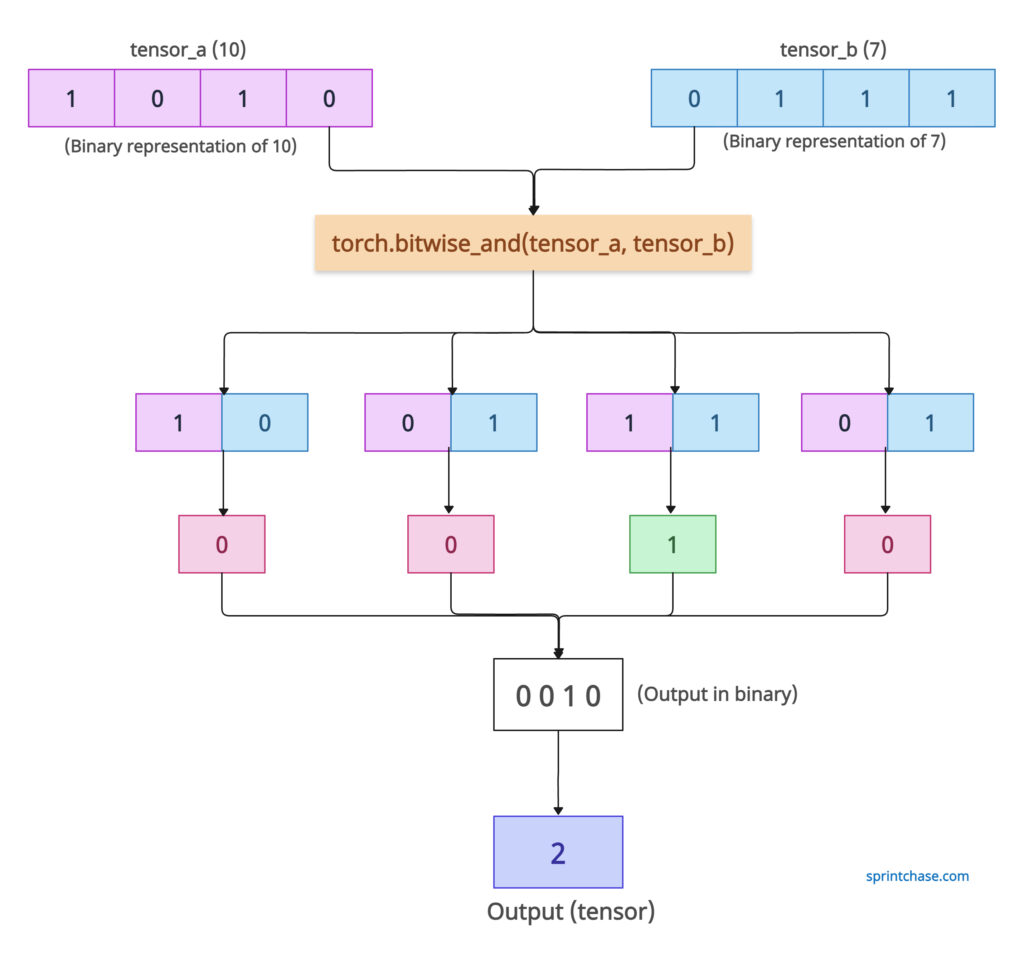
For example, in the above figure, we have a tensor(10) and a tensor(7), and we performed a bitwise_and operation. This is an operation performed on a tensor with only one element. There can be multiple elements.
Here is the explanation:
The binary of the first tensor 10 is 1010.
The binary of the second tensor 7 is 0111.
Now, compare the first bits of both tensors: 1 and 0. Then, check the above table. If input A is 1 and input B is 0, the output is 0.
Now, check the second bits of both the tensors: 0 and 1, and the output is 0.
For the third element of both tensors, 1 and 1, the output is 1.
For the fourth element of both tensors, 0 and 1, the output is 0.
That means the output is (0 0 1 0). And it is a binary representation of the integer 2. So, the output tensor will be tensor(2). This is the main logic behind the bitwise_and method.
Syntax
torch.bitwise_and(input, other, out=None)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| input (Tensor) | It represents an input tensor. The first tensor. |
| other (Tensor or Scalar, optional) | It represents the second input tensor or a scalar value to perform the bitwise AND with. |
| out (Tensor, optional) |
It is an output tensor to store the result. |
Element-wise bitwise AND between two tensors
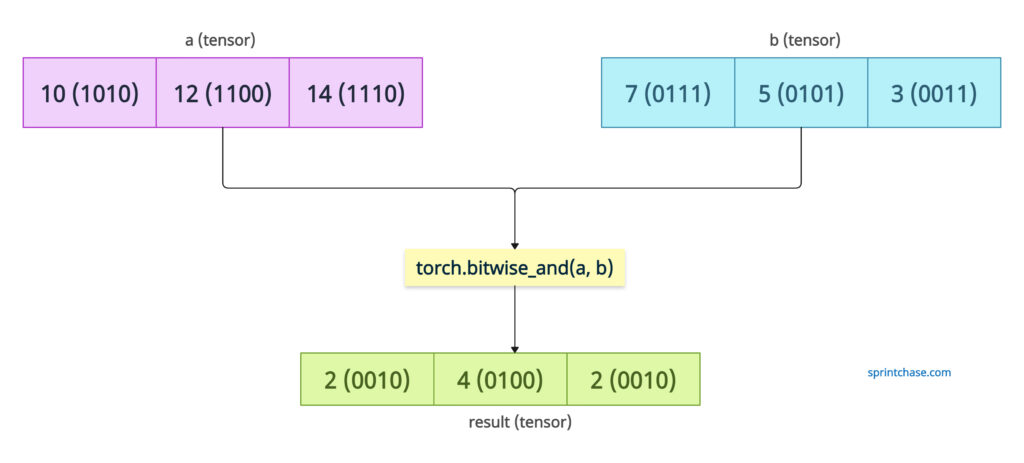
Let’s define two tensors with three elements each and perform a bitwise AND operation between the corresponding elements of the two tensors.
import torch # Define two integer tensors a = torch.tensor([10, 12, 14]) # Binary: [1010, 1100, 1110] b = torch.tensor([7, 5, 3]) # Binary: [0111, 0101, 0011] # Perform bitwise AND result = torch.bitwise_and(a, b) print(result) # Output: tensor([2, 4, 2]) # Binary: [0010, 0100, 0010]
Based on the previously defined logic, 10 and 7 return 2, 12 and 5 return 4, and 14 and 3 return 2.
Bitwise AND with a Scalar
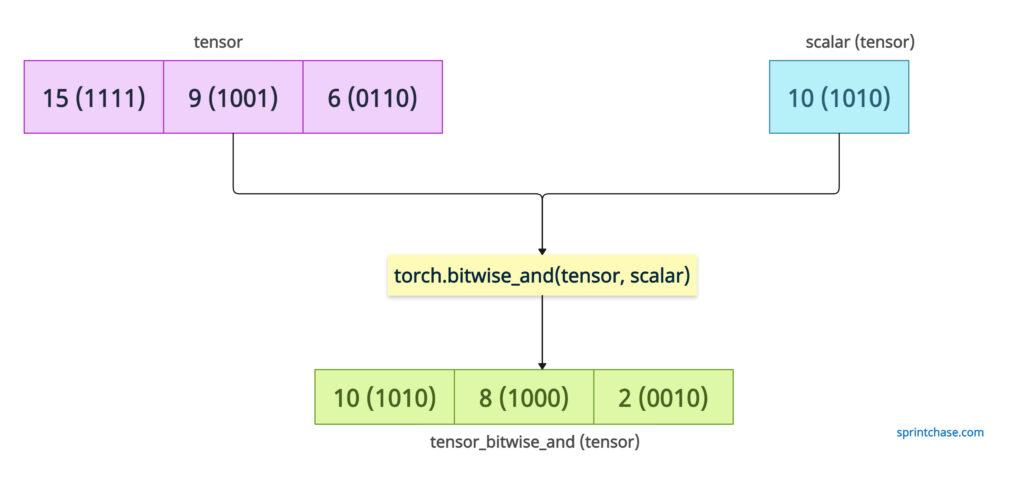
If the first value is a tensor and the second value is a scalar, the .bitwise_and() method applies a bitwise AND operation between a tensor and a scalar value.
import torch tensor = torch.tensor([15, 9, 6]) # Binary: [1111, 1001, 0110] scalar = 10 # Binary: 1010 # Perform bitwise AND with scalar tensor_bitwise_and = torch.bitwise_and(tensor, scalar) print(tensor_bitwise_and) # Output: tensor([10, 8, 2])
Boolean tensors
Let’s define two boolean tensors containing True and False values and perform the bitwise_and operation.
import torch boolean_a = torch.tensor([True, False, True, False]) boolean_b = torch.tensor([False, True, True, False]) # Perform element-wise logical AND operation result_and = torch.bitwise_and(boolean_a, boolean_b) print(result_and) # Output: tensor([False, False, True, False])The result will be only True if both elements are True. Otherwise, it will be False.
Unsupported Types
If your input tensor contains unsupported types (e.g., floating-point tensors), it will throw an error.
import torch
# Define floating-point tensors
a = torch.tensor([10.0, 12.0])
b = torch.tensor([7.0, 5.0])
try:
result = torch.bitwise_and(a, b)
except RuntimeError as e:
print(e)
# Output: "bitwise_and_cpu" not implemented for 'Float'
It only accepts integer-based tensor types. It does not work with floating points or complex numbers.