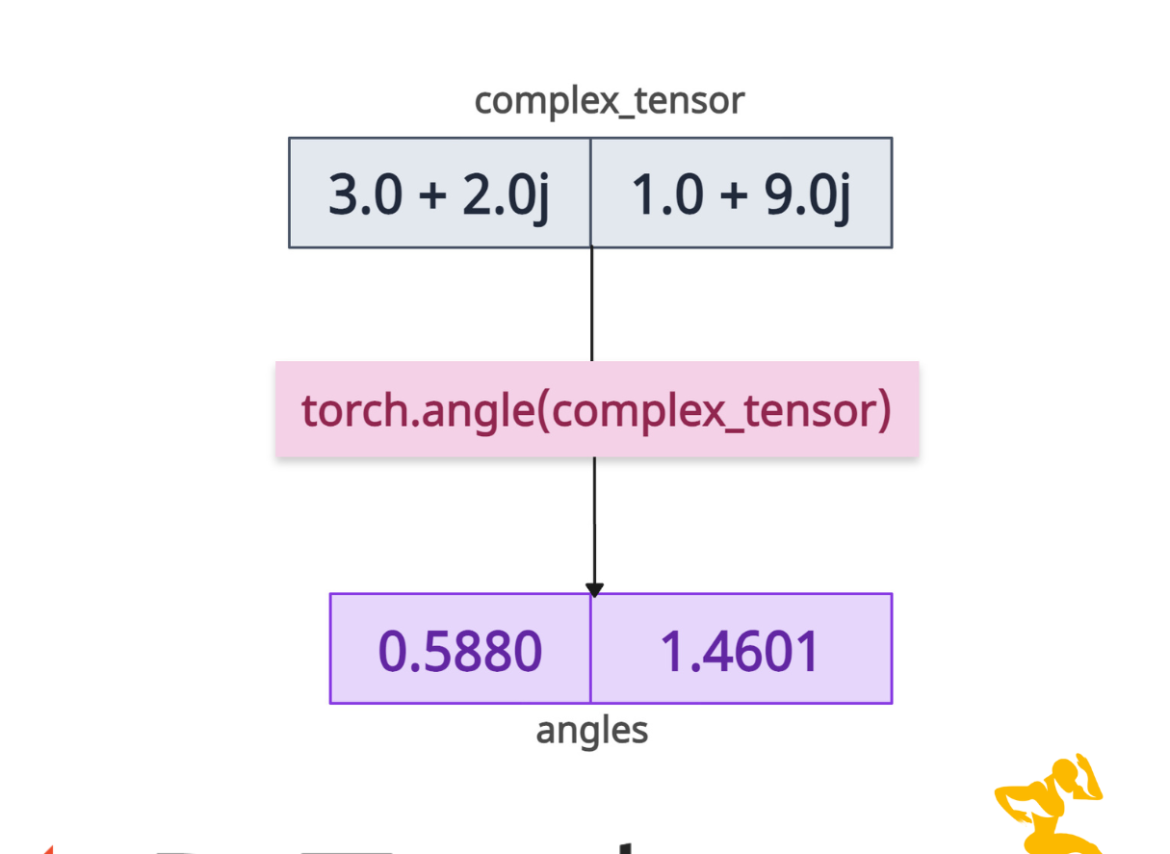
The torch.angle() method calculates the element-wise angle (or phase) of each element in the input tensor.
The output is a tensor of the same shape as the input, containing the angles (in radians) of the complex numbers.
For a complex number z = a + bj, the angle is θ = atan2(b, a), which determines the direction of z in the complex plane.
- Positive real numbers: Angle = 0
- Negative real numbers: Angle = π (180°)
- Purely imaginary numbers: Angle = ±π/2
For real-valued inputs, it returns a tensor of zeros, as real numbers lie on the real axis with no phase.
The output is always in the interval (-π, π].
Syntax
torch.angle(input, out=None)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| input (Tensor) | It represents an input tensor, which can be of type torch.complex64 or torch.complex128 for complex numbers, or a real-valued tensor (e.g., torch.float32, torch.float64). |
| out (Tensor, optional) |
It is an output tensor to store the result. |
Complex number
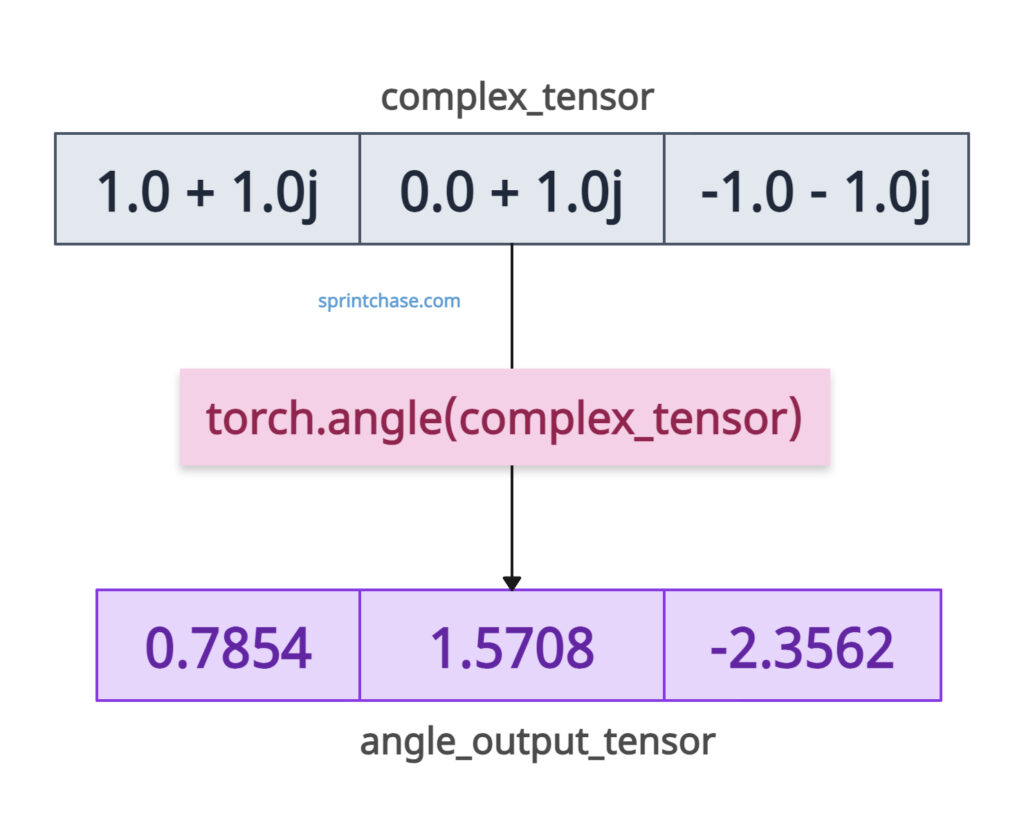
Let’s calculate the phase of a complex tensor.import torch
complex_tensor = torch.tensor([1.0 + 1.0j, 0.0 + 1.0j, -1.0 - 1.0j],
dtype=torch.complex64)
angle_output_tensor = torch.angle(complex_tensor)
print(angle_output_tensor)
# Output: tensor([ 0.7854, 1.5708, -2.3562])
# Angles in radians (~ [π/4, π/2, -3π/4])
PyTorch uses atan2(imag, real) under the hood to ensure the correct quadrant.
Let me explain how this works:
1.0 + 1.0j
This value is the first quadrant of the complex plane:
- Real part: 1.0
- Imag part: 1.0
- Angle: arctangent(imag / real) = arctan(1 / 1) = π/4 ≈ 0.7854
0.0 + 1.0j
This value lies directly on the positive imaginary axis.
- Real part: 0.0
- Imag part: 1.0
- Angle = π/2 ≈ 1.5708
-1.0 – 1.0j
This value lies in the third quadrant (negative real, negative imag).
- Real part: -1.0
- Imag part: -1.0
- Angle = arctan(imag / real) = arctan(1 / 1) + π = -3π/4 ≈ -2.3562
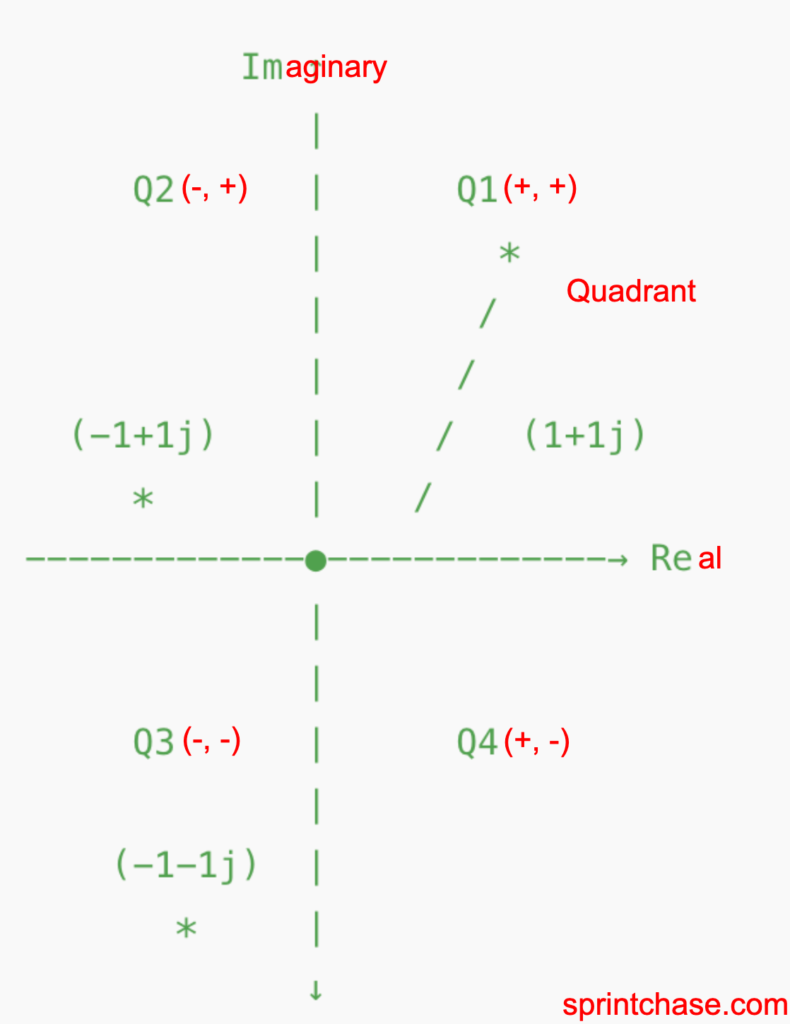
In the above figure, you can start measuring the angle from the positive real axis counterclockwise.
Real number input
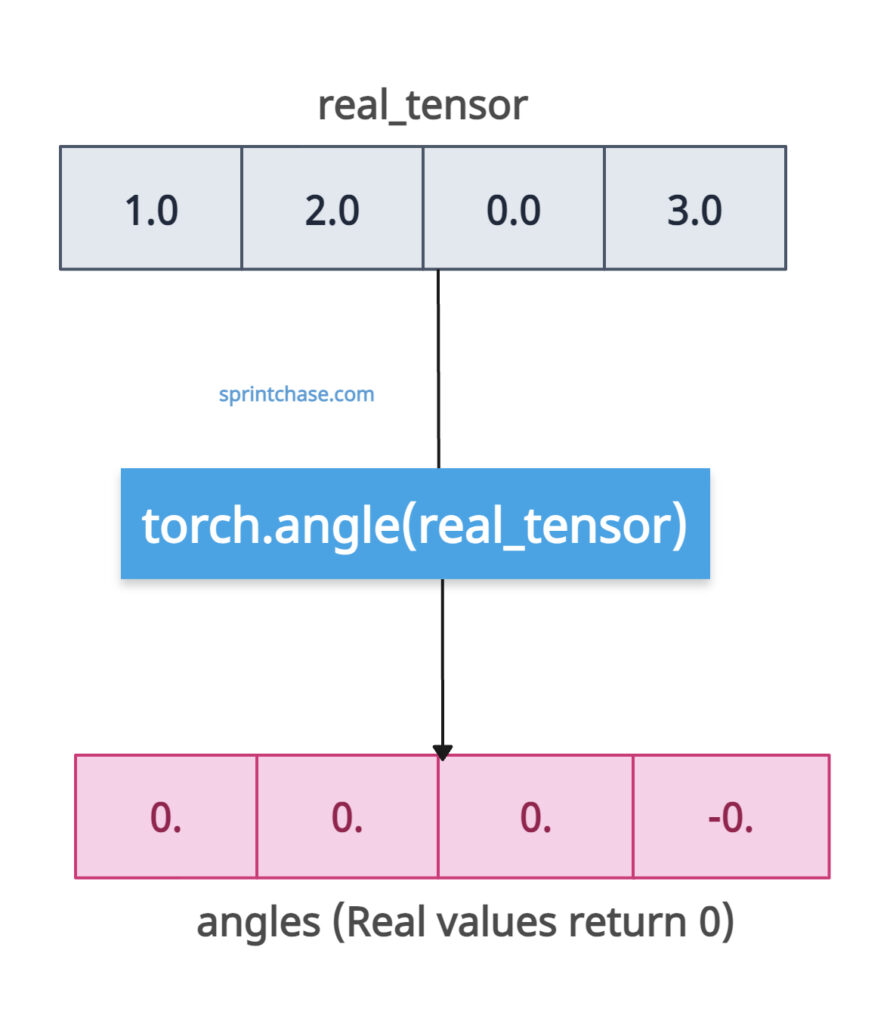
Since real numbers have no imaginary component, the phase is always 0.
import torch real_tensor = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0, 0.0, 3.0]) angles = torch.angle(real_tensor) print(angles) # Output: tensor([0., 0., 0., 0.])
2D Complex Tensor
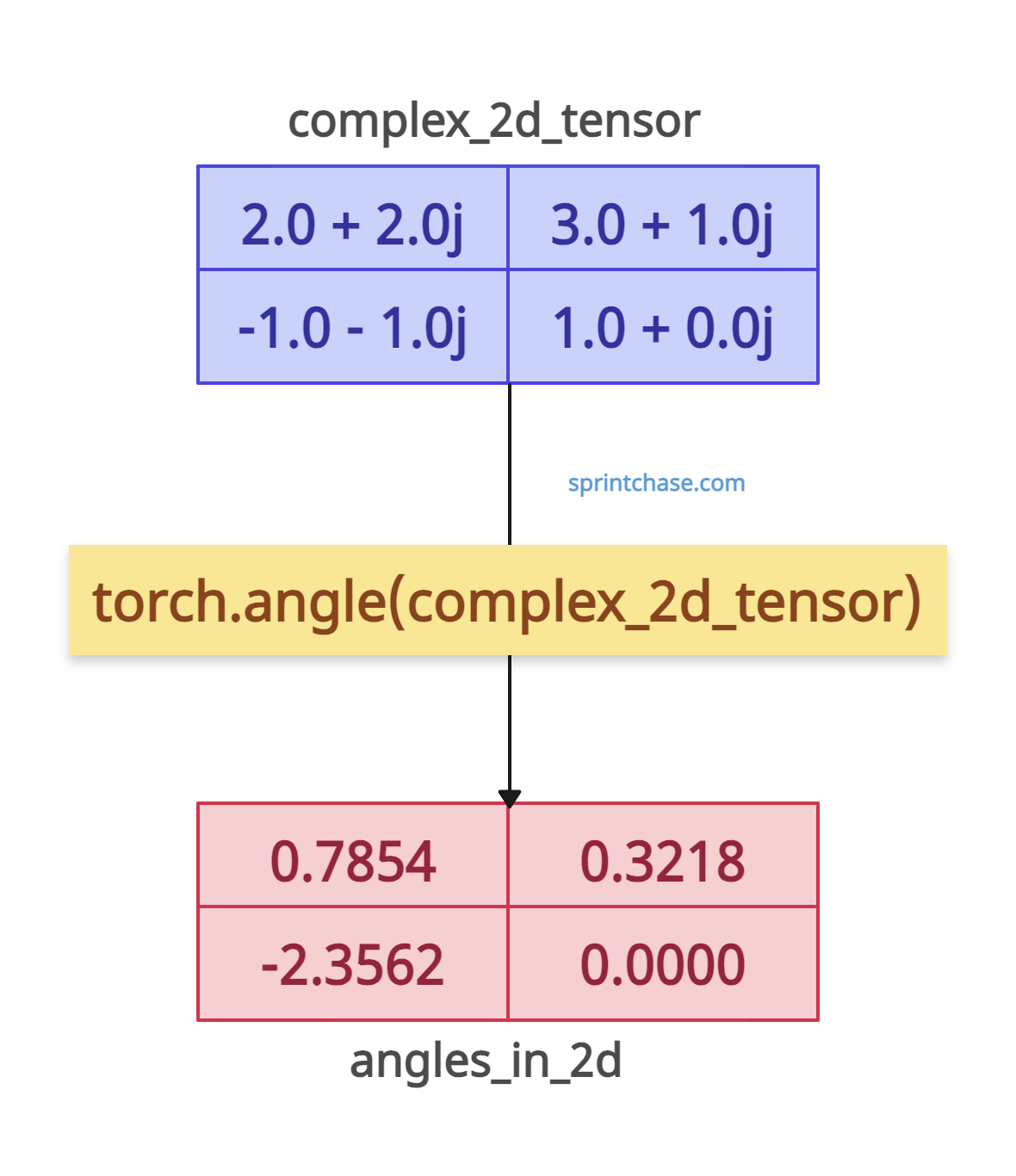
Since this method operates element-wise, it preserves the input tensor’s shape and calculates the phase for each complex number.
import torch
complex_2d_tensor = torch.tensor([[2.0 + 2.0j, 3.0 + 1.0j], [-1.0 - 1.0j, 1.0 + 0.0j]],
dtype=torch.complex64)
angles_in_2d = torch.angle(complex_2d_tensor)
print(angles_in_2d)
# Output:
# tensor([[ 0.7854, 0.3218],
# [-2.3562, 0.0000]])
That’s all!