PyTorch tensors are similar to the Numpy arrays but can run on GPUs and support automatic differentiation. Pandas DataFrames, on the other hand, are tables with rows and columns, where each column can have a different data type.
Our main task is to take data from Tensors and put it into a DataFrame structure.
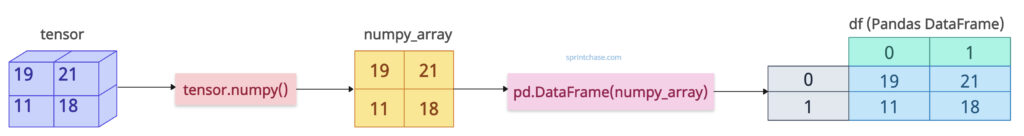
The easiest way to convert PyTorch tensors to Pandas DataFrame is to convert a tensor into a numpy array using the .numpy() method and then convert the numpy array to a DataFrame using the pd.DataFrame() constructor.
import torch import pandas as pd tensor = torch.tensor([[19, 21], [11, 18]]) numpy_array = tensor.numpy() df = pd.DataFrame(numpy_array) print(df) # Output # 0 1 # 0 19 21 # 1 11 18
The above conversion is basic. We assumed we were working on a CPU instead of a GPU, which is a CPU without gradients.
Handling GPU Tensors
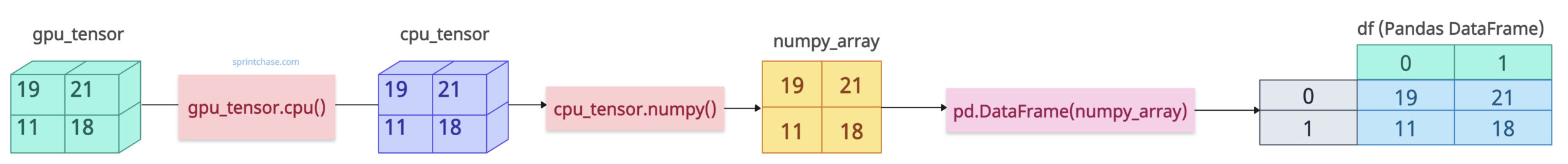
If you are working with GPU, the first step is to move the tensor from GPU to CPU using the .cpu() method.
In the next step, convert the tensor into a numpy array using the .numpy() method.
At last, convert that numpy array into a data frame using pd.DataFrame() method.
import torch import pandas as pd gpu_tensor = torch.tensor([[19, 21], [11, 18]]).cuda() cpu_tensor = gpu_tensor.cpu() numpy_array = cpu_tensor.numpy() df = pd.DataFrame(numpy_array) print(df) # Output: # 0 1 # 0 19 21 # 1 11 18
Data Type Conversions
You can change the data type of your tensor values by passing the “dtype” argument. For example, if you want your tensor to be floating-point values, you can pass dtype=torch.float32 while creating a tensor.
import torch
import pandas as pd
# Converting a tensor to float
tensor = torch.tensor([[11, 18], [19, 21]],
dtype=torch.float32)
# Converting to NumPy Array
numpy_array = tensor.numpy()
# Converting Numpy Array to Pandas DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(numpy_array)
# Print DataFrame
print(df)
# Output
# 0 1
# 0 11.0 18.0
# 1 19.0 21.0
You can see that the output DataFrame has float values.
Detaching Gradients
What if a tensor is a part of the computation graph, it would have gradients. In that case, we need to detach the gradients first using the .detach() method and then convert the tensor to a numpy array and the numpy array to a data frame.
import torch
import pandas as pd
# Converting a tensor to float
tensor = torch.tensor([[11, 18], [19, 21]],
dtype=torch.float32, requires_grad=True)
# Detaching tensor from computation graph
tensor_detached = tensor.detach()
# Converting to NumPy Array
numpy_array = tensor_detached.numpy()
# Converting Numpy Array to Pandas DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(numpy_array)
# Print DataFrame
print(df)
# Output
# 0 1
# 0 11.0 18.0
# 1 19.0 21.0
Converting 1D Tensor to DataFrame (Column/Row)
As a column
import torch import pandas as pd tensor_1d = torch.tensor([11, 19, 18, 21]) # As a column df_col = pd.DataFrame(tensor_1d.numpy()) # Print DataFrame print(df_col) # Output # 0 # 0 11 # 1 19 # 2 18 # 3 21
As a row
import torch import pandas as pd tensor_1d = torch.tensor([11, 19, 18, 21]) numpy_array = tensor_1d.numpy() # Reshaping the array to row array_row = numpy_array.reshape(1, -1) # Converting to data frame df_row = pd.DataFrame(array_row) # Print DataFrame print(df_row) # Output # 0 1 2 3 # 0 11 19 18 21
3D Tensor to 2D DataFrame
Create a 3D tensor with shapes (2, 3, 4), which means 2 depth slices, each containing 3 rows and 4 columns. First, we need to reshape a tensor from 3D to 2D.
For that, we can use the .view(-1, tensor.shape[-1]) function to flatten the first two dimensions (2 * 3 = 6 rows, 4 columns).
Now, convert that 2D tensor to a numpy array using the .numpy() method.
In the last step, pass that numpy array to pd.DataFrame() function to create a DataFrame out of it.
import torch
import pandas as pd
# Creating a 3D tensor of shape (2, 3, 4)
tensor_3d = torch.tensor([
[[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12]], # First depth slice
[[13, 14, 15, 16], [17, 18, 19, 20], [21, 22, 23, 24]] # Second depth slice
])
# Reshaping the 3D tensor to 2D
# Flatten depth & rows into one dimension
tensor_2d = tensor_3d.view(-1, tensor_3d.shape[-1])
# Convert to NumPy array
numpy_array = tensor_2d.numpy()
# Create DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(numpy_array)
# Print DataFrame
print(df)
# Output:
# 0 1 2 3
# 0 1 2 3 4
# 1 5 6 7 8
# 2 9 10 11 12
# 3 13 14 15 16
# 4 17 18 19 20
# 5 21 22 23 24
Assigning Column and Index Labels
While converting to a DataFrame, you can pass the “columns” and “index” arguments to the pd.DataFrame() function for setting the column names and row indices for your final DataFrame.
import torch
import pandas as pd
# Initializing a 2D tensor
tensor = torch.tensor([[19, 21], [11, 18]])
# Converting a 2D tensor to numpy array
numpy_array = tensor.numpy()
# Converting numpy array to Pandas DataFrame with column names and row indices
df = pd.DataFrame(numpy_array,
columns=["Feature1", "Feature2"],
index=["Sample1", "Sample2"])
# Printing DataFrame
print(df)
# Output:
# Feature1 Feature2
# Sample1 19 21
# Sample2 11 18
The above-commented output shows that the new columns for the data frame are Feature1 and Feature2. The row indices are Sample1 and Sample2.
Non-Contiguous Tensors
If you are working with a non-contiguous tensor, you should convert it to a contiguous one using the .contiguous() function and then create a conversion.
import torch import pandas as pd # Non-contiguous tensor non_contig = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]).t() # Transposed (non-contiguous) # Make contiguous conti_tensor = non_contig.contiguous() # Convert it to numpy array numpy_array = conti_tensor.numpy() # Converting numpy array to Pandas DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame(numpy_array) # Printing DataFrame print(df) # Output: # 0 1 # 0 1 3 # 1 2 4That’s all!