The efficient way to create a 1D tensor using a loop in PyTorch is to pre-allocate the tensor using torch.empty() method and then fill the values via a loop. The .empty() method creates an uninitialized tensor of a specified size.
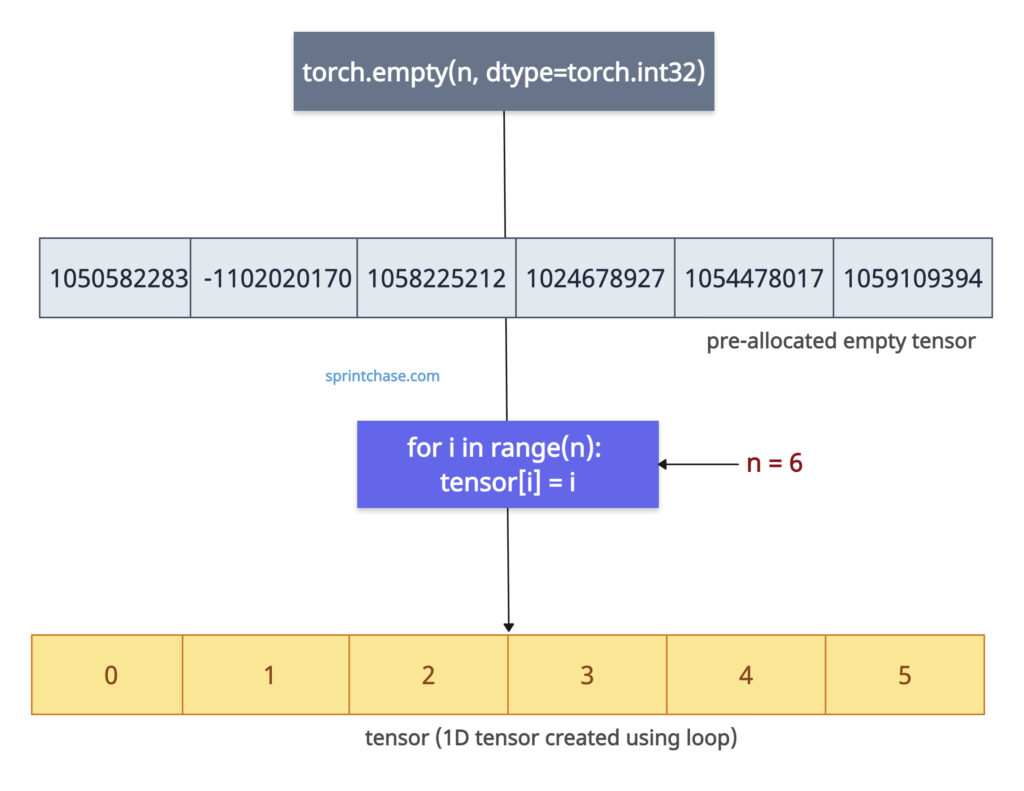
The main advantage of this approach is that you don’t need to create a tensor each time in the loop. The tensor is only made once, during pre-allocating, and then we append the values to it using a loop.
import torch
# Number of elements
n = 6
tensor = torch.empty(n, dtype=torch.int32)
for i in range(n):
tensor[i] = i
print(tensor)
# Output: tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5], dtype=torch.int32)
You can also use torch.zeros() for pre-allocating. And you can specify dtype explicitly. For example, you might want to create a tensor of float values.
For a large data creation, Prefer PyTorch’s vectorized operation function such as torch.arange(). If the tensor size is known in advance, then this approach is helpful.Conditional Filling
First, we pre-allocate an empty tensor and then assign the values to that tensor based on the condition. (e.g., even/odd indices).
import torch
n = 5
tensor = torch.zeros(n)
for i in range(n):
tensor[i] = 1 if i % 2 == 0 else 0
print(tensor)
# Output: tensor([1., 0., 1., 0., 1.])
In this code, if the input value is even, 1.0 is assigned, and if it is odd, 0.0 is assigned in the tensor. The final tensor would be filled with either 1.0 or 0.0.
For vectorized conditional operations, always use torch.where() method.
List Comprehension
If you are iterating using a for loop, in that scenario, you can also use a list comprehension. First, you can generate a list of your specified size and then convert it to a tensor with just one line. Easy peasy!
import torch tensor = torch.tensor([i for i in range(6)], dtype=torch.float64) print(tensor) # Output: tensor([0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5.], dtype=torch.float64)
You can see that we created a tensor of float64 values in a single line of code using torch.tensor() and list comprehension.
Using a for loop and list append()
If you don’t want to use list comprehension, you can use a for loop to create a list of specified elements and then convert that list into a tensor using torch.tensor() method.
import torch
empty_list = []
for i in range(7):
empty_list.append(i)
tensor = torch.tensor(empty_list)
print(tensor)
# Output: tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
print(tensor.dtype)
# Output: torch.int64
That’s all!