To convert a PyTorch tensor of ints to a tensor of booleans, use the .bool() method on the input tensor, and it returns the masked tensor containing False for the zero value and True for the positive or negative value.
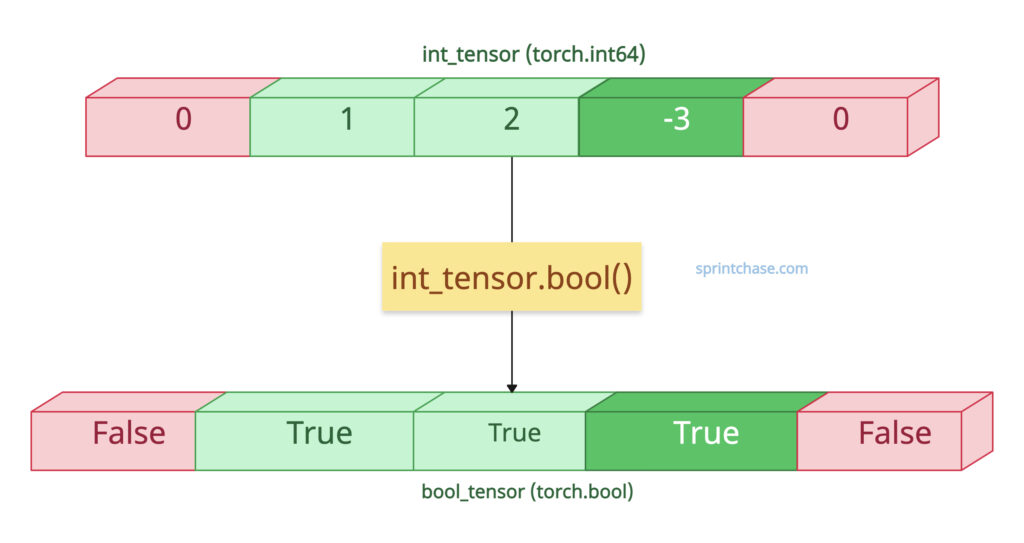
Negative values are treated as True since they are not zero. Only zeros are treated as False in a Boolean context.
It works on tensors of any shape and integer dtype (e.g., int8, int16, int32, int64).
The type of a Boolean tensor is torch.bool. We can verify the conversion by getting the type of a tensor using the dtype property.
import torch int_tensor = torch.tensor([0, 1, 2, -3, 0], dtype=torch.int64) print(int_tensor.dtype) # Output: torch.int64 bool_tensor = int_tensor.bool() print(bool_tensor) # Output: tensor([False, True, True, True, False]) print(bool_tensor.dtype) # Output: torch.bool
In the above code, we defined an int64 tensor and printed its type, which is torch.int64.
In the next step, we converted that int_tensor into a bool_tensor using the .bool() method.
After the conversion, we again printed the type, which is torch.bool.
2D (or Higher-Dimensional) Tensor
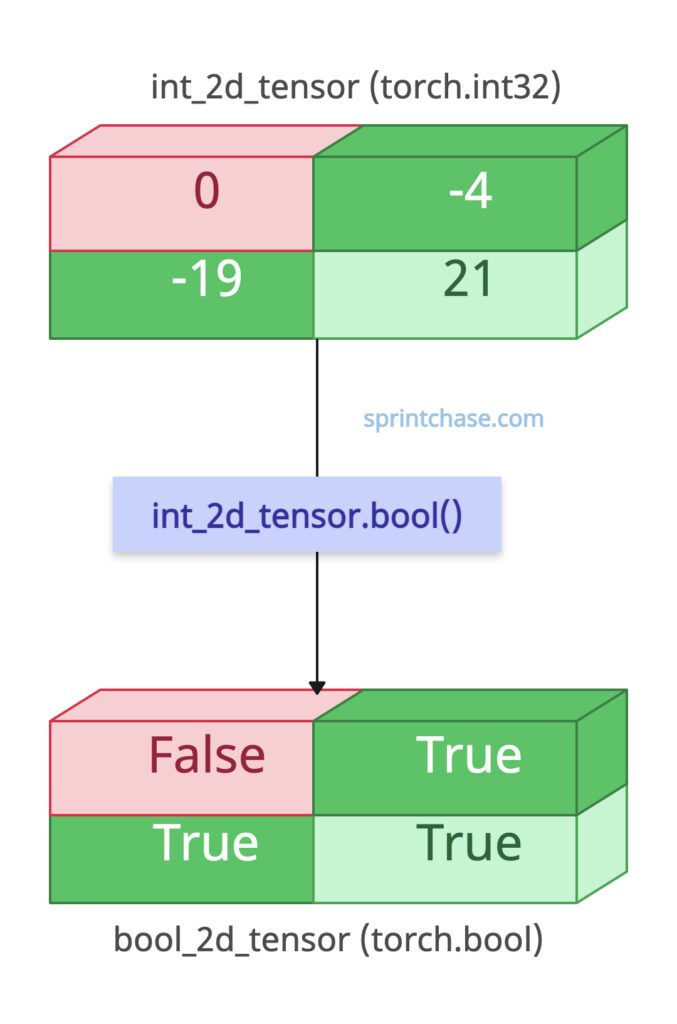
If the input tensor is 2D or higher-dimensional, the output tensor will have the same dimension and shape. It can’t return the output in a different shape.
import torch
int_2d_tensor = torch.tensor([[0, -4],
[-19, 21]], dtype=torch.int32)
print(int_2d_tensor.dtype)
# Output: torch.int32
bool_2d_tensor = int_2d_tensor.bool()
print(bool_2d_tensor)
# Output: tensor([[False, True],
# [ True, True]])
print(bool_2d_tensor.dtype)
# Output: torch.bool
The above code shows that the input tensor and output tensor have the same shape. The output values have been masked to either True or False based on the input tensor’s values.
Scalar tensor
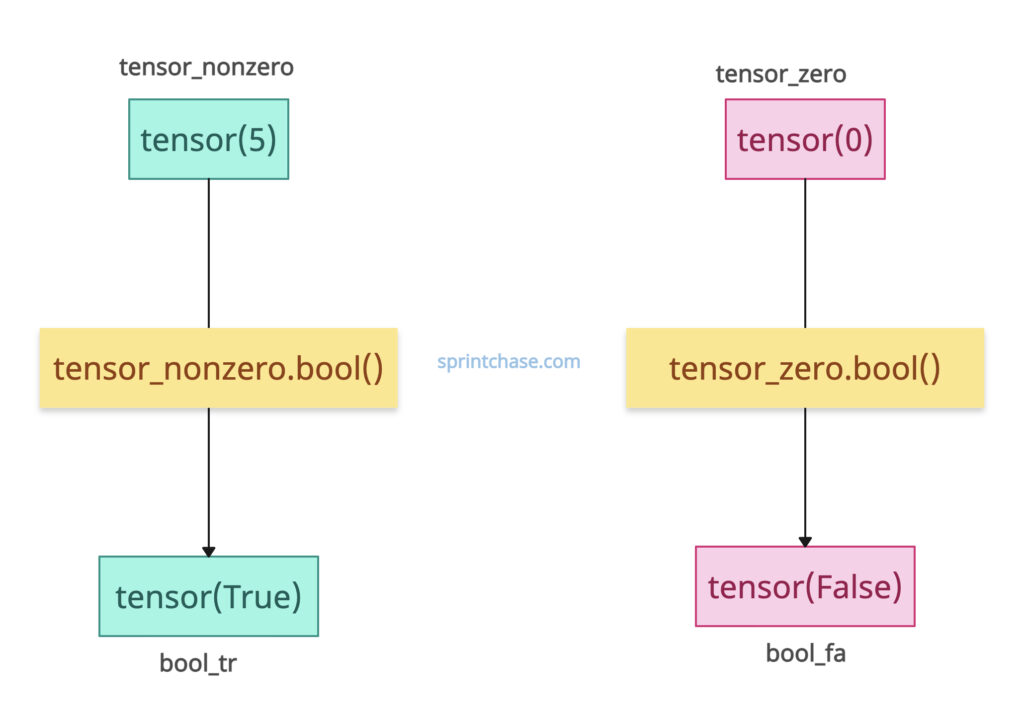
Scalar tensor means a tensor with only a single value.
When the input value is a scalar tensor, it will convert to a 0D boolean scalar tensor.
If the input value is tensor(0), the output is a tensor(False); otherwise, if it is positive or negative, the output is a tensor(True).
import torch tensor_nonzero = torch.tensor(5, dtype=torch.int32) bool_tr = tensor_nonzero.bool() print(bool_tr) # Output: tensor(True) tensor_zero = torch.tensor(0, dtype=torch.int32) bool_fa = tensor_zero.bool() print(bool_fa) # Output: tensor(False)
Empty tensor
If no elements are present in the input tensor, the output boolean tensor will also be empty.
import torch empty_tensor = torch.tensor([], dtype=torch.int32) print(empty_tensor) # Output: tensor([], dtype=torch.int32) print(empty_tensor.dtype) # Output: torch.int32 bool_tensor = empty_tensor.bool() print(bool_tensor) # Output: tensor([], dtype=torch.bool) print(bool_tensor.dtype) # Output: torch.bool
That’s all!





