The torch.tile() method creates a new tensor by repeating the input tensor based on the repetition factors specified in the “dims” argument. It does not modify the original tensor.
This method’s main advantage is allowing element-wise repeating along multiple dimensions. It also provides flexibility in customizing the output tiled tensor.
It supports extra dimensions beyond the input tensor’s shape. However, due to memory usage, be cautious with large tensors.
Syntax
torch.tile(input, dims)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| input (Tensor) | It is an input tensor whose elements are to be repeated. |
| dims (tuple) |
It is a tuple of integers specifying repetitions along each dimension. If len(dims) > input.dim(), singleton dimensions are added to the input tensor’s shape before tiling. |
Tiling a 1D Tensor
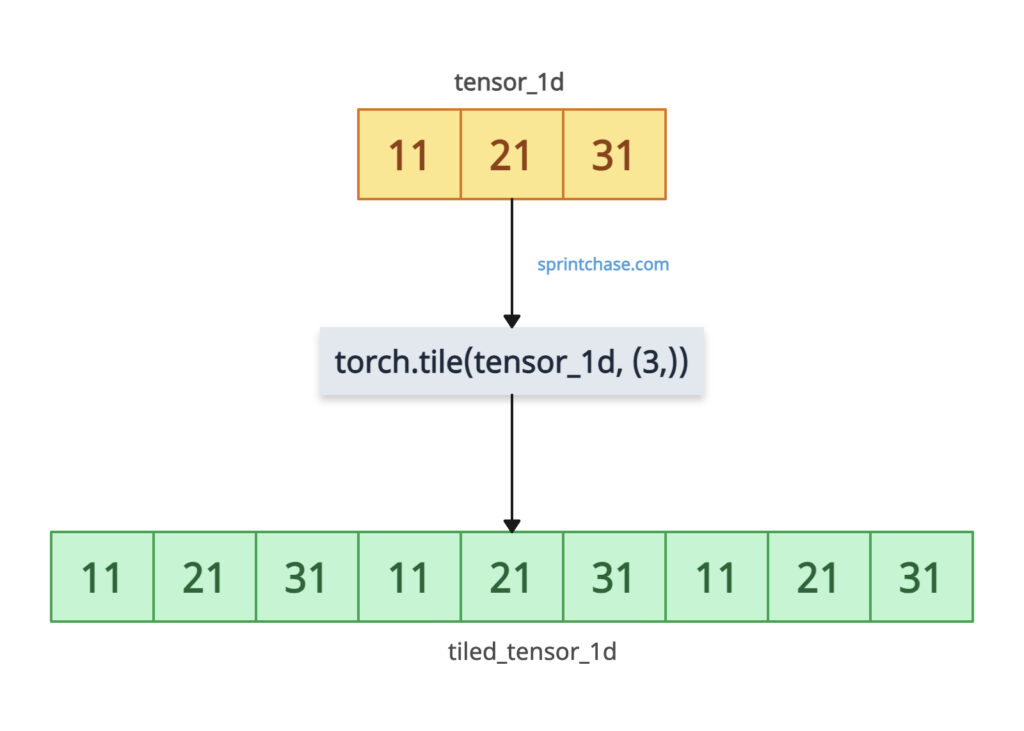
Let’s define the 1D tensor using torch.tensor() method and create a new tensor filled with repeated elements 3 times of the input tensor.
import torch tensor_1d = torch.tensor([11, 21, 31]) tiled_tensor_1d = torch.tile(tensor_1d, (3,)) print(tiled_tensor_1d) # Output: tensor([11, 21, 31, 11, 21, 31, 11, 21, 31])
In the above code, the output tiled_tensor_1d has repeated 11, 21, and 31 elements three times.
Tiling a 2D Tensor
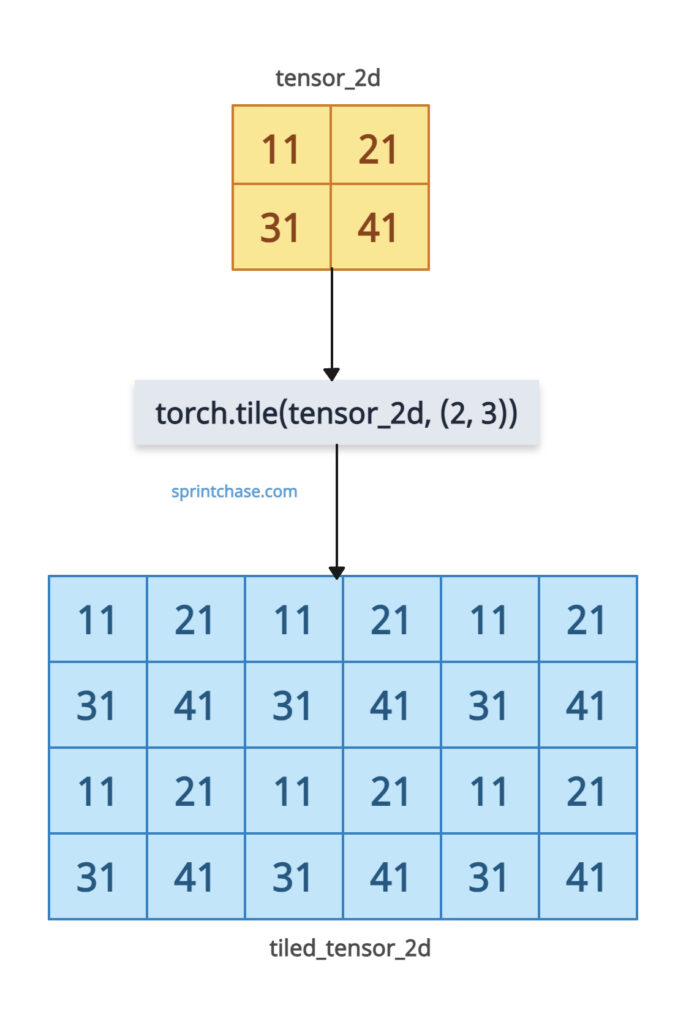
Let’s repeat a 2D tensor along specific dimensions.
import torch tensor_2d = torch.tensor([[11, 21], [31, 41]]) tiled_tensor_2d = torch.tile(tensor_2d, (2, 3)) print(tiled_tensor_2d) # Output: # tensor([[11, 21, 11, 21, 11, 21], # [31, 41, 31, 41, 31, 41], # [11, 21, 11, 21, 11, 21], # [31, 41, 31, 41, 31, 41]])
Here, we passed a dims tuple (2, 3), which means we tiled 2 times along dim 0 (rows) and 3 times along dim 1(columns), resulting in a (4, 6) tensor. Each [11, 21] and [31, 41] row is repeated as specified.
Tiling with extra dimensions
You can use more repetition factors than the tensor’s dimensions.
import torch tensor_1d = torch.tensor([10, 20]) # Tile with extra dimensions (3 new dims, repeat 2, 2, 3 times) tiled_tensor = torch.tile(tensor_1d, (2, 2, 3)) print(tiled_tensor) # Output: # tensor([[[10, 20, 10, 20, 10, 20], # [10, 20, 10, 20, 10, 20]], # [[10, 20, 10, 20, 10, 20], # [10, 20, 10, 20, 10, 20]]])
In the above code, the 1D tensor [1, 2] is treated as having shape (1, 1, 2) (adding singleton dimensions).
It is then tiled twice along the first dimension, twice along the second, and three times along the third, producing a (2, 2, 6) tensor.
Tiling with Zero
If you try to repeat 0 times, it will return an empty tensor with the corresponding dimension size set to 0.
import torch tensor = torch.tensor([11, 12]) # Tile with 0 repetitions (empty tensor) zeroed_tensor = torch.tile(tensor, (0,)) print(zeroed_tensor) # Output: tensor([], dtype=torch.int64) print(zeroed_tensor.shape) # Output: torch.Size([0])
Scalar tensor
import torch scalar_tensor = torch.tensor(21) scalar_tiled = torch.tile(scalar_tensor, (2, 3)) print(scalar_tiled) # Output: # tensor([[21, 21, 21], # [21, 21, 21]]) print(scalar_tiled.shape) # Output: torch.Size([2, 3])
3D tensor
Let’s initialize a 3D tensor using tensor.ones() method and repeat along various dimensions.
import torch tensor_3d = torch.ones(2, 1, 3) tiled_3d_tensor = torch.tile(tensor_3d, (3, 4, 2)) print(tiled_3d_tensor.shape) # Output: torch.Size([6, 4, 6])
That’s it!





