What do you mean by an empty tensor? It is not necessarily about values (though that can be relevant), but primarily about the shape. An empty tensor has a shape where at least one of the dimensions is zero.
For example, a tensor with shape (0, 3) or (2, 0, 5) would be considered empty because one of its dimensions is zero. A tensor with shape (2, 2) or (3, 3, 1) is not empty because none of its dimensions is zero.
So, we are looking at the tensor’s “shape.” If any dimension of a tensor is 0, the total number of elements would be zero.
Creating an empty
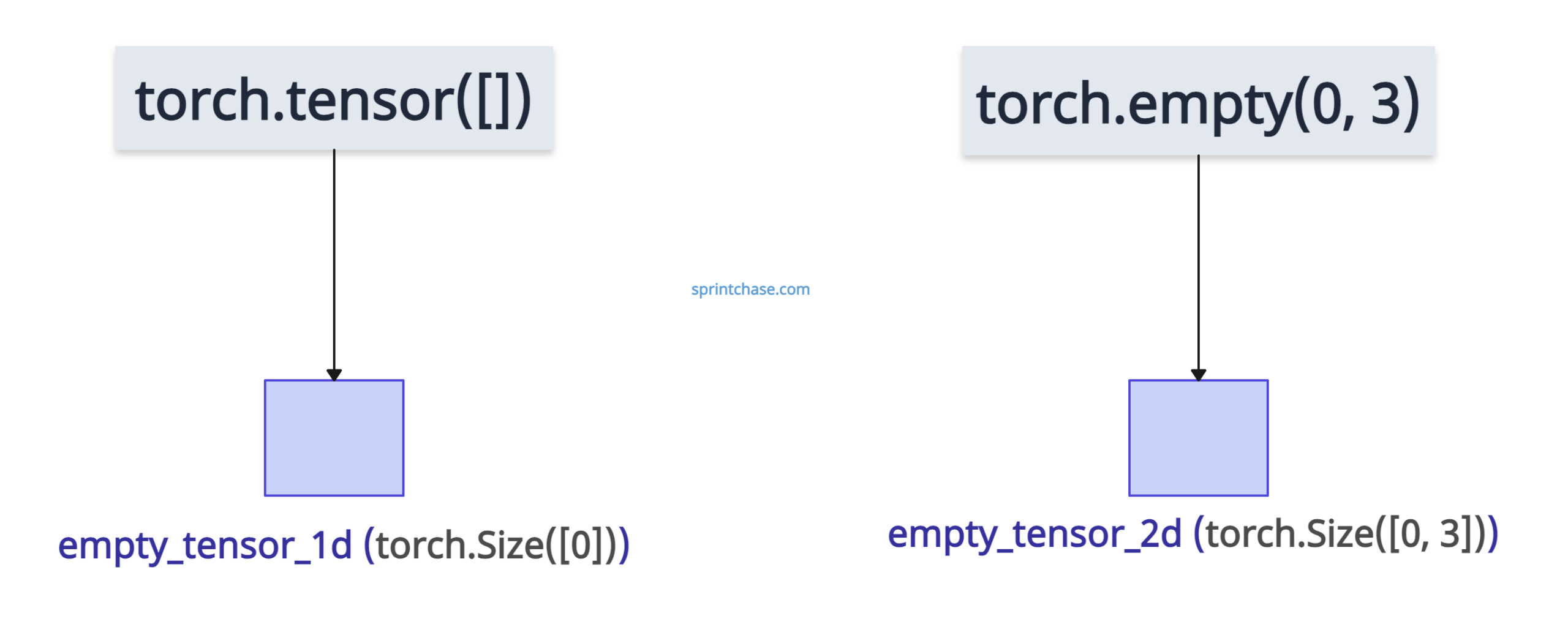
To create an empty tensor efficiently in PyTorch, you can use torch.tensor([]) method for creating 1D tensor and torch.empty() method for creating a multidimensional empty tensor.
import torch empty_tensor_1d = torch.tensor([]) print(empty_tensor_1d) # Output: tensor([]) print(empty_tensor_1d.shape) # Output: torch.Size([0]) empty_tensor_2d = torch.empty(0, 3) print(empty_tensor_2d) # Output: tensor([], size=(0, 3)) print(empty_tensor_2d.shape) # Output: torch.Size([0, 3])
In the above program, you can see that we used both methods to create empty tensors, which are truly “empty” as they contain no data.
The .empty() method behaves differently internally. It allocates memory for a tensor of a specified shape but does not initialize the values. This differentiates it from a zero-size tensor, which may contain uninitialized (garbage) data.
How to check if a tensor is empty
The most accurate way to check if a tensor is empty in PyTorch is by using a tensor.numel() == 0 condition.
The .numel() method returns the total number of elements in the tensor. If it’s greater than 0, the tensor is non-empty. Otherwise, it is empty.
import torch tensor = torch.tensor([]) print(tensor.numel() == 0) # Output: True
In the above code, we have checked for the 1D tensor, which returns True, which means it is empty.
Let’s check for a non-empty tensor:import torch tensor = torch.tensor([3]) print(tensor.numel() == 0) # Output: False
Checking 2D tensor
 Let’s create a 2D tensor with shape (0, 5) and check for its emptiness.
Let’s create a 2D tensor with shape (0, 5) and check for its emptiness.
import torch # Create a 2D tensor with shape (0, 5) tensor = torch.empty((0, 5)) print(tensor.numel() == 0) # Output: TrueLet’s create a non-empty 2D tensor and check the same:

import torch # Create a 2D tensor with shape (2, 3) non_empty_tensor = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) print(non_empty_tensor.numel() == 0) # Output: False
Checking 3D tensor
To check for an empty 3D tensor in PyTorch, use the .numel() method and see if it returns 0. If it returns 0, the tensor is empty; otherwise, it is not.
import torch
# Sample 3D tensors
empty_tensor = torch.empty((0, 4, 5)) # Shape (0, 4, 5)
non_empty_tensor = torch.tensor([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]],
[[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]]) # Shape (2, 2, 3)
# Function to check if a tensor is empty
def is_empty(tensor):
return tensor.numel() == 0
# Function to check if a tensor is non-empty
def is_non_empty(tensor):
return tensor.numel() > 0
# Checking the tensors
print(is_empty(empty_tensor)) # True
print(is_non_empty(empty_tensor)) # False
print(is_empty(non_empty_tensor)) # False
print(is_non_empty(non_empty_tensor)) # True
Check the tensor’s shape
The tensor.shape returns the shape of the current tensor.import torch
tensor = torch.tensor([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]],
[[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]])
print(tensor.shape)
# Output: torch.Size([2, 2, 3])
If we somehow determine that within the size, finding 0 means that one dimension is empty, and the tensor is empty. But how are we gonna do that? By using the “in” operator.
import torch
tensor = torch.tensor([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]],
[[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]]])
if 0 in tensor.shape:
print("Tensor is empty")
else:
print("Tensor is not empty")
# Tensor is not empty
We can clearly see that the tensor is not empty. But check out this:
import torch
tensor = torch.empty((2, 0, 3))
if 0 in tensor.shape:
print("Tensor is empty")
else:
print("Tensor is not empty")
# Tensor is empty
That’s it!