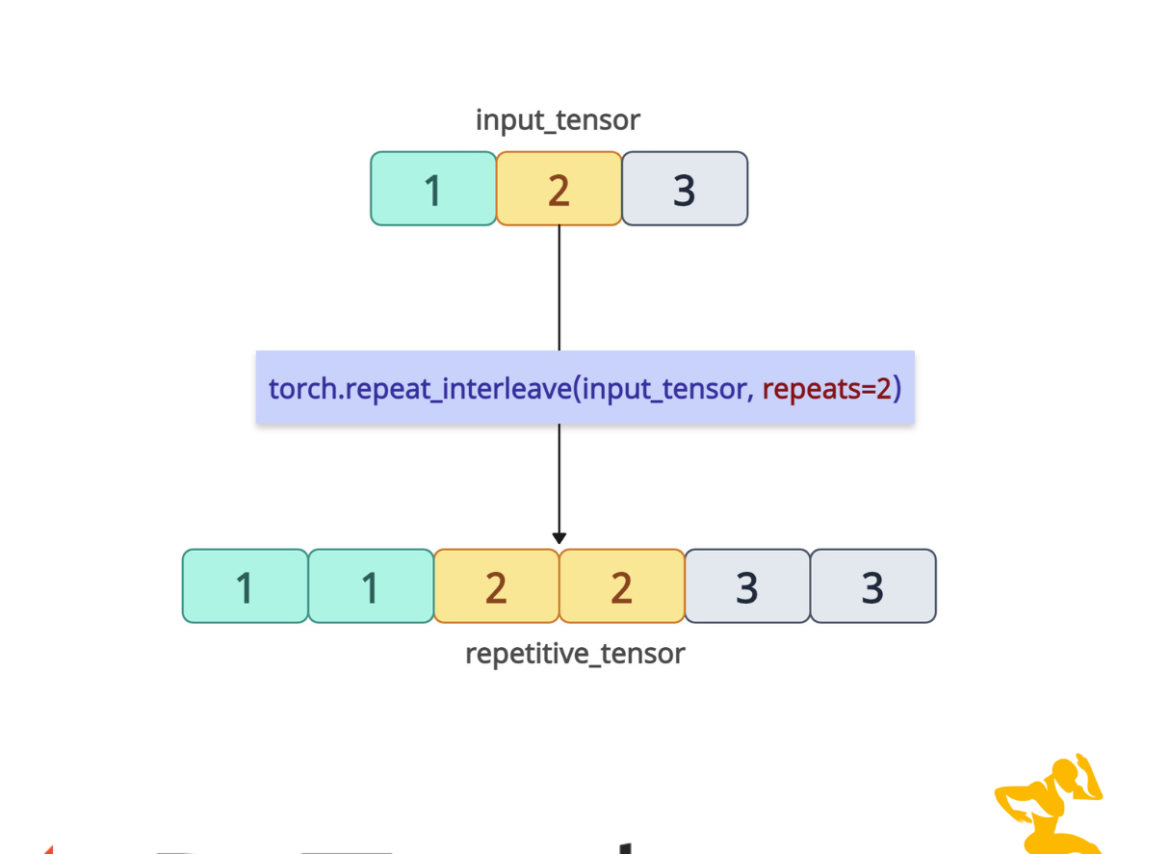
The torch.repeat_interleave() method repeats elements of a tensor along a specified dimension according to the provided repetition counts. It duplicates individual elements contiguously, which is essential for data augmentation and tensor reshaping.
Syntax
torch.repeat_interleave(input, repeats, dim=None, output_size=None)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| input (Tensor) | It represents an input tensor. |
| repeats (Tensor or int) |
It represents the number of repetitions for each element. It can broadcast to fit the shape of the given axis. If it is a 1D tensor, it element-wise repeats. |
| dim (int, optional) |
It is the dimension along which to repeat elements. If dim is None, the input tensor is flattened before repeating. |
| output_size (int, optional) | It represents the total size of the output tensor along the repeated dimension. |
Element repetition (1D Tensor)
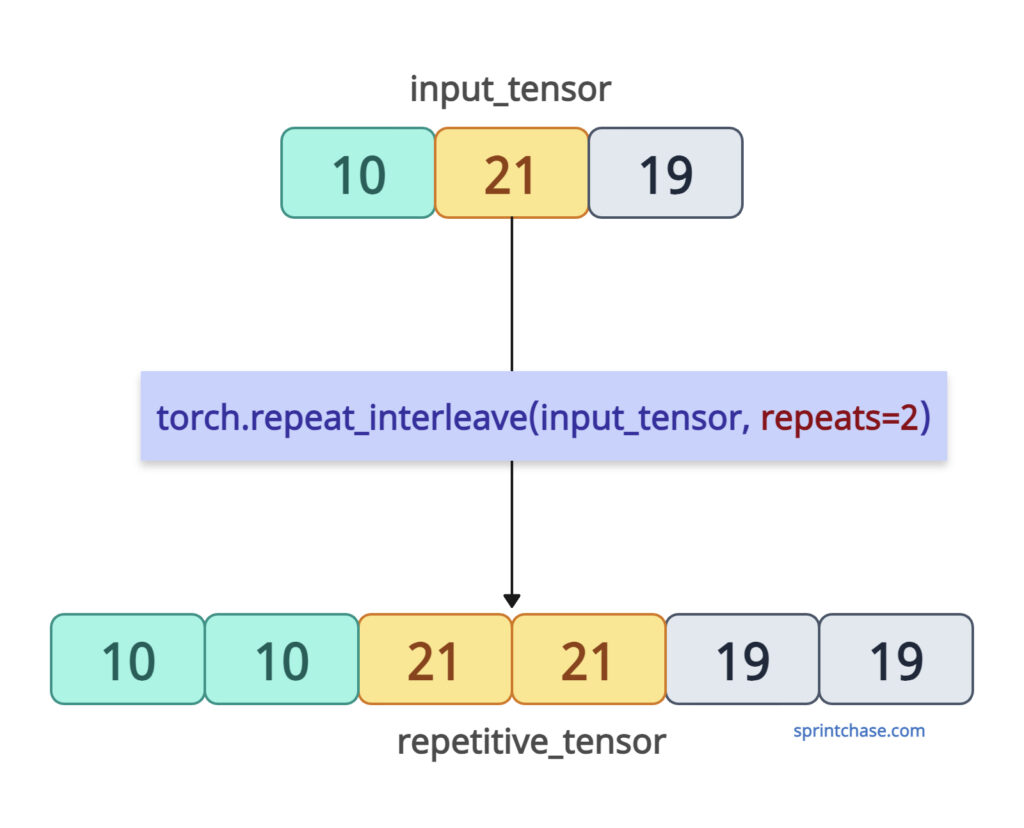
Let’s define a 1D tensor and repeat each element twice.
import torch input_tensor = torch.tensor([10, 21, 19]) repetitive_tensor = torch.repeat_interleave(input_tensor, repeats=2) print(repetitive_tensor) # Output: tensor([10, 10, 21, 21, 19, 19])
Since dim=None, the output tensor is flattened.
Along a specific dimension
Repeating along rows
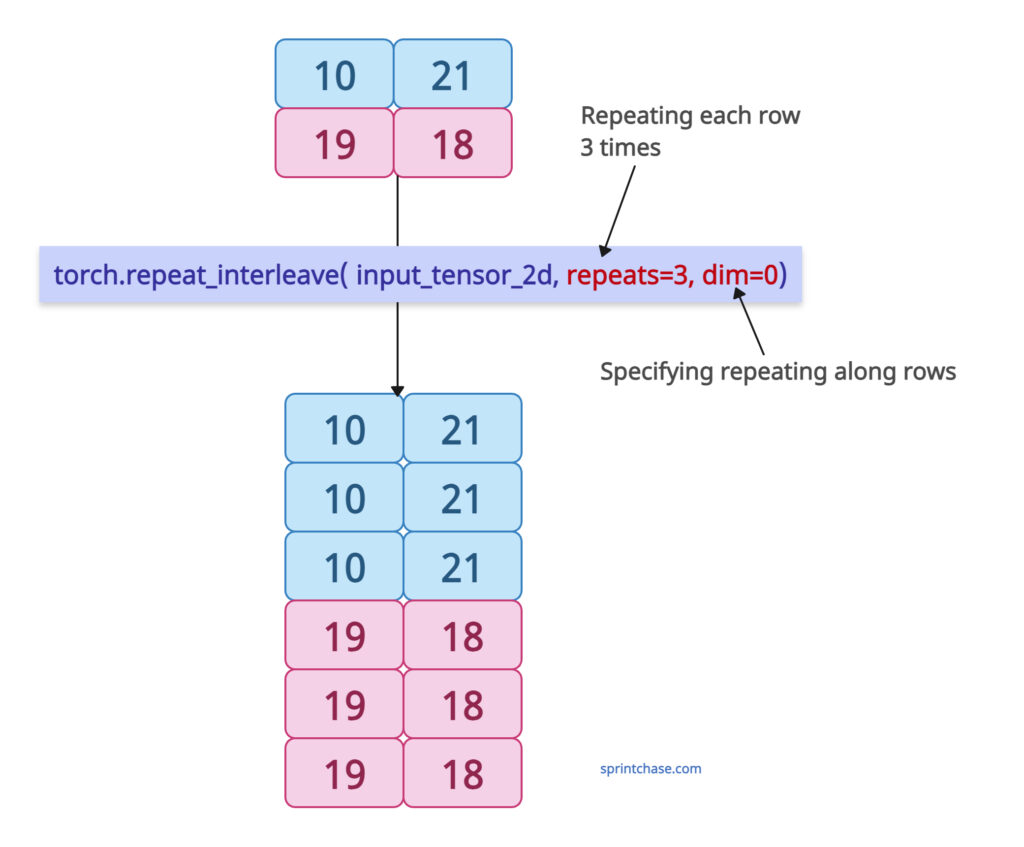
Let’s define a 2D tensor and repeat the elements along the rows by passing dim=0. That means it will repeat each row three times if you pass repeats=3.
import torch
input_tensor_2d = torch.tensor([[10, 21],
[19, 18]])
print(input_tensor_2d)
# Output:
# tensor([[10, 21],
# [19, 18]])
repetitive_tensor_rows = torch.repeat_interleave(
input_tensor_2d,
repeats=3,
dim=0)
print(repetitive_tensor_rows)
# Output:
# tensor([[10, 21],
# [10, 21],
# [10, 21],
# [19, 18],
# [19, 18],
# [19, 18]])
You can see that the first row of the tensor [10, 21] is repeated thrice, and the second row of the input tensor [19, 18] is also repeated thrice.
Repeating along columns
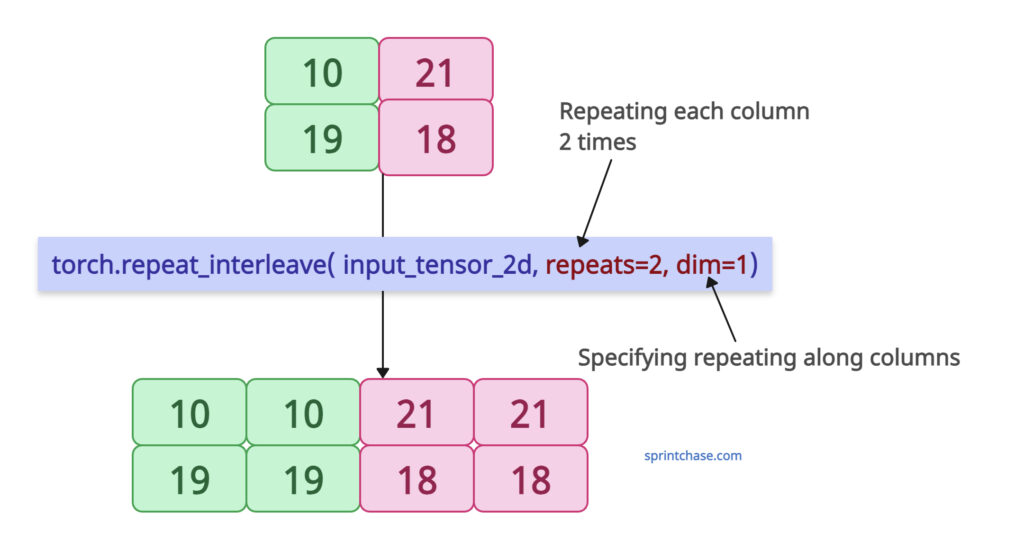
To repeat along columns, we need to pass dim=1.
Let’s define a 2D tensor and repeat the columns twice.
import torch
input_tensor_2d = torch.tensor([[10, 21],
[19, 18]])
print(input_tensor_2d)
# Output:
# tensor([[10, 21],
# [19, 18]])
repetitive_tensor_columns = torch.repeat_interleave(
input_tensor_2d,
repeats=2,
dim=1)
print(repetitive_tensor_columns)
# Output:
# tensor([[10, 10, 21, 21],
# [19, 19, 18, 18]])
The above output shows that we repeated the first and second columns of the input tensor twice in the output tensor.
Variable repetition with tensor repeats
We can repeat elements of a 1D tensor with different repetition counts. For that, we need to pass repeats as a tensor instead of a single integer.
import torch input = torch.tensor([11, 21, 31]) repeats = torch.tensor([1, 3, 2]) output = torch.repeat_interleave(input, repeats) print(output) # Output: tensor([11, 21, 21, 21, 31, 31])
In this code, we repeat the first element once, the second element three times, and the third element twice.
Flattening behavior with dim=None
Let’s define a 2D tensor and demonstrate the default behavior when dim is not specified. Spoiler alert, it will flatten the output tensor.
import torch input = torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4]]) output = torch.repeat_interleave(input, repeats=2, dim=None) print(output) # Output: tensor([1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4])
You can see that the output tensor is not 2D; it is 1D, which means flattened.
Using output_size for Optimization
When you know the output tensor’s size in advance, you can specify the output size for performance using the “output_size” argument.
import torch input = torch.tensor([1, 2]) repeats = torch.tensor([2, 4]) fixed_size_tensor = torch.repeat_interleave(input, repeats, output_size=6) print(fixed_size_tensor) # Output: tensor([1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2])
In this code, we pre-defined the output tensor’s size to 6. Therefore, the size of the repeated elements does not exceed 6.
If you do, it will throw an error like this: RuntimeError: allocated size does not match required size
Now, the first element is repeated twice, and the second element is repeated four times. The total size is 6. So, it gives the proper repetitive tensor.
That’s all!