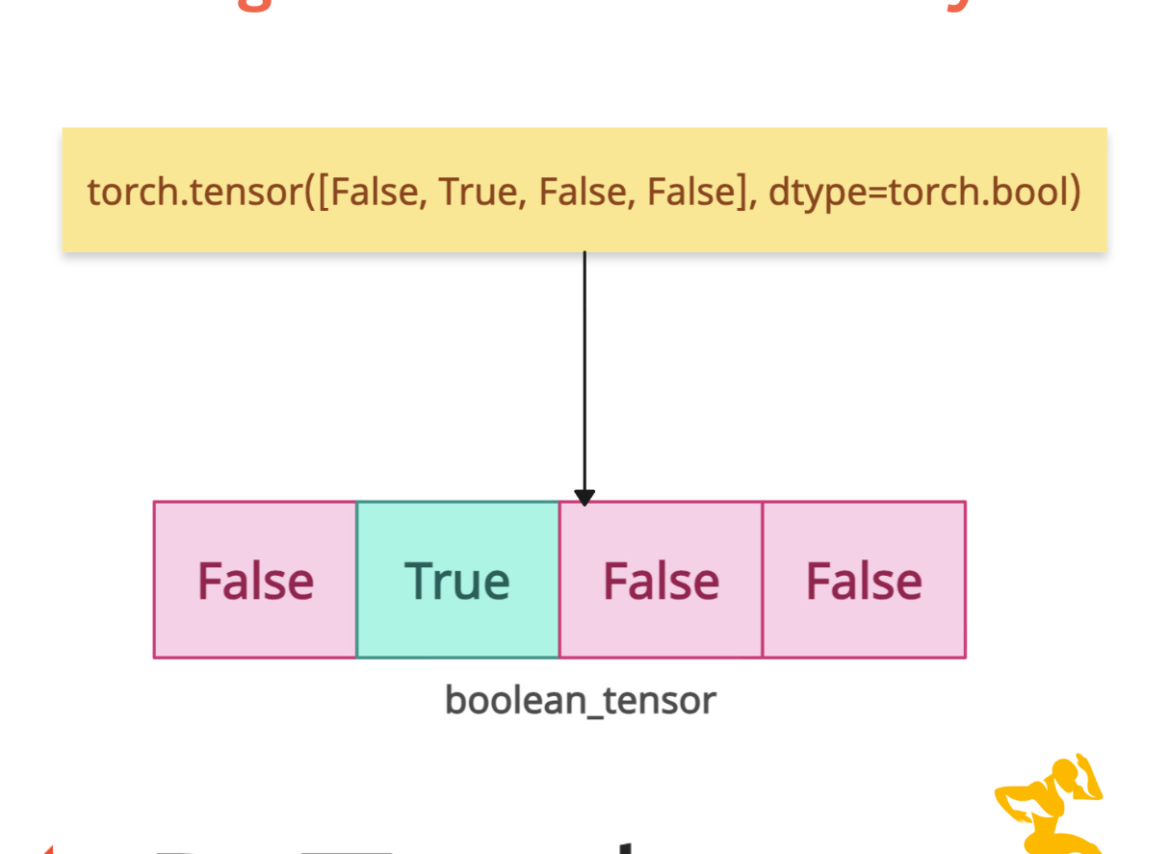
To create a Boolean tensor efficiently in PyTorch, use the torch.tensor() method and pass the dtype=torch.bool explicitly (inferred if data is bools), where each element holds a True or False value.
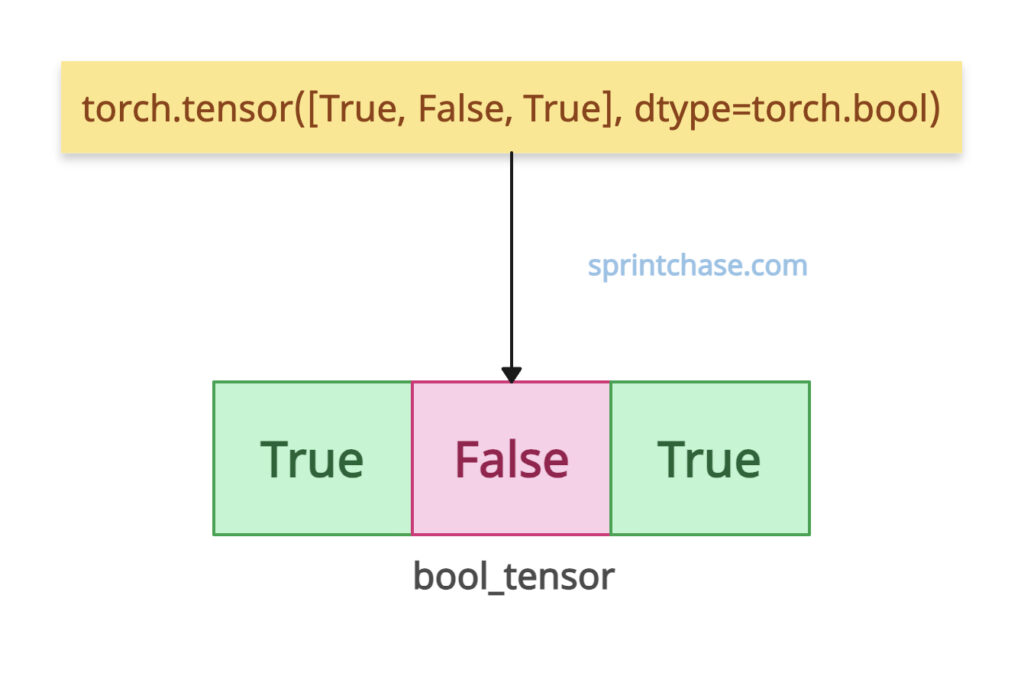
import torch bool_tensor = torch.tensor([True, False, True], dtype=torch.bool) print(bool_tensor) # Output: tensor([ True, False, True], dtype=torch.bool)
You can use this boolean tensor for masking, condition checks, logical operations, or indexing.
Tensor initialization methods
Generating All False using torch.zeros()
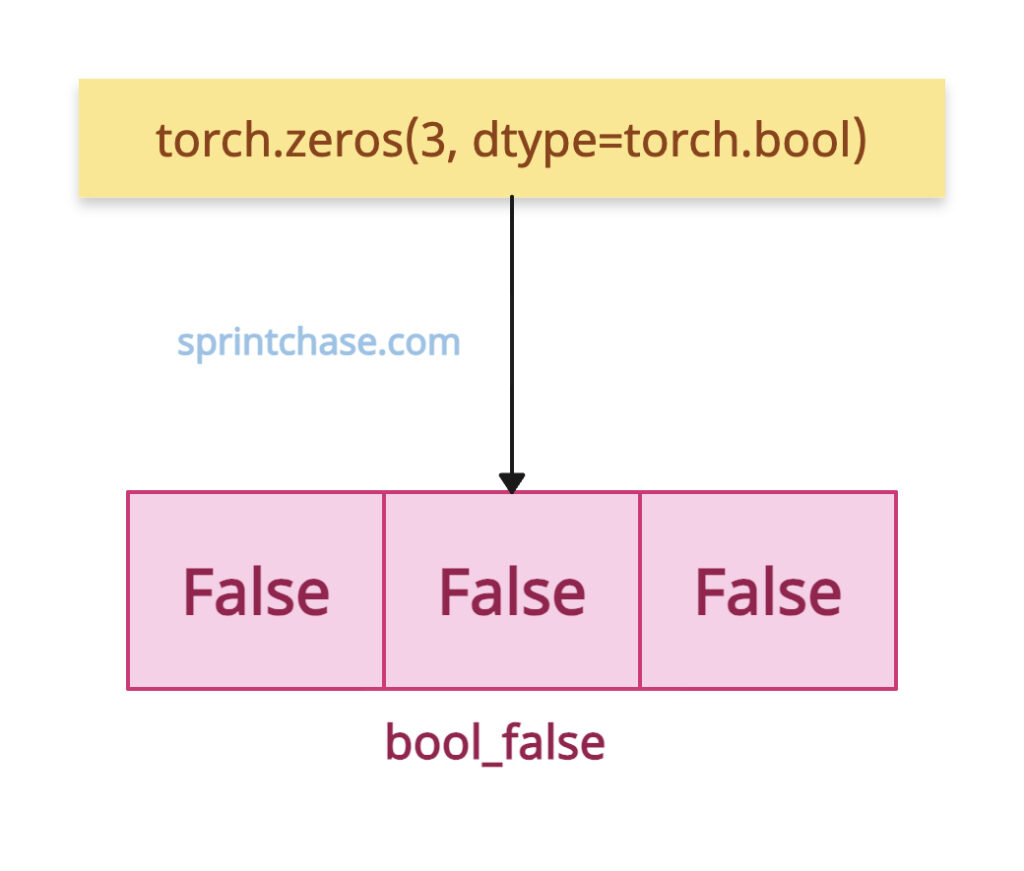
If you want to create a Boolean tensor where each value is False, you can use torch.zeros() method.
import torch bool_false = torch.zeros(3, dtype=torch.bool) print(bool_false) # Output: tensor([False, False, False])
In this code, we created a Boolean tensor with three elements, all of which are False.
Generating All True using torch.ones()
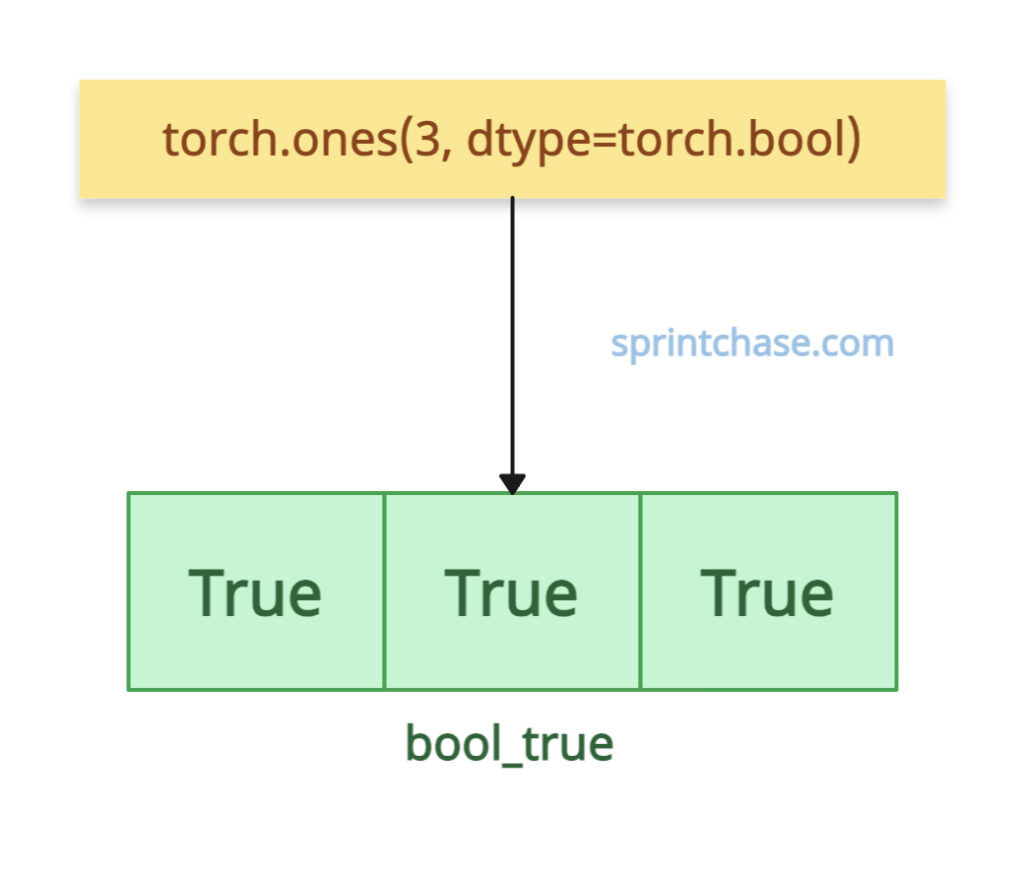 If you want to create a Boolean tensor where each value is True, you can use torch.ones() method.
If you want to create a Boolean tensor where each value is True, you can use torch.ones() method.
import torch bool_true = torch.ones(3, dtype=torch.bool) print(bool_true) # Output: tensor([ True, True, True])In this code, we created a Boolean tensor with three elements, all of which are True.
Fill with a value using torch.full()
 Using torch.full() method, you can create a Boolean tensor of either True values or False.
Using torch.full() method, you can create a Boolean tensor of either True values or False.
import torch bool_full_true = torch.full((4,), True, dtype=torch.bool) print(bool_full_true) # Output: tensor([True, True, True, True]) bool_full_false = torch.full((4,), False, dtype=torch.bool) print(bool_full_false) # Output: tensor([False, False, False, False])
In this code, we created both True and False-valued tensors.
That’s all!