The torch.linalg.det() method calculates the determinant of a square matrix. The determinant is a scalar value that provides important properties of a matrix, such as whether it is invertible (non-zero determinant) or singular (zero determinant).
This method is mainly used for checking matrix invertibility. It helps us analyze eigenvalues and matrix properties in machine learning and scientific computing.
For a 2×2 matrix [[a, b], [c, d]], the determinant is calculated as: ad – bc.Syntax
torch.linalg.det(A, out=None)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| A (Tensor) | It is a tensor of shape (*, n, n), where * is zero or more batch dimensions, and n is the size of the square matrix. |
| out (Tensor, optional) |
It is the output tensor to store the result. |
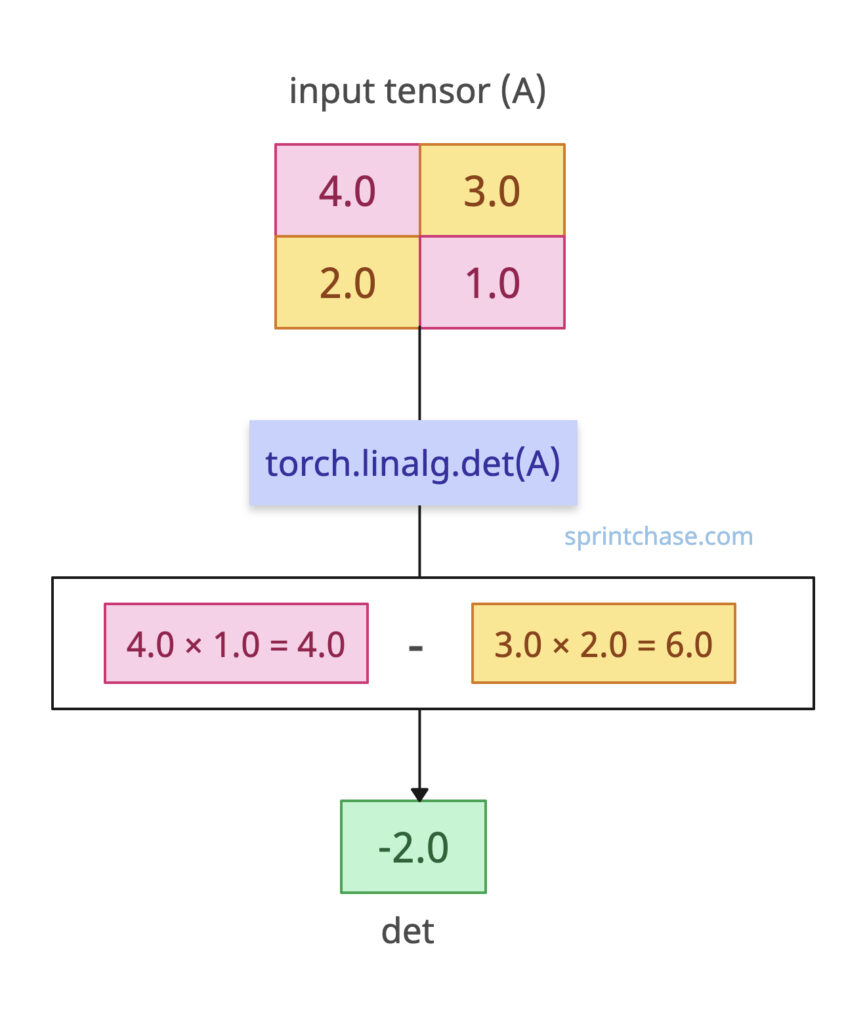
Determinant of a Single 2×2 Matrix
Let’s define a 2×2 tensor and find its determinant.import torch
A = torch.tensor([[4.0, 3.0],
[2.0, 1.0]])
det = torch.linalg.det(A)
print(det)
# Output: tensor(-2.0)
You must be wondering why the output is tensor(-2.0). Let’s find out: Here, 4 × 1 – 3 × 2 = 4 – 6 = -2. A non-zero determinant indicates the matrix is invertible.
Identity Matrix
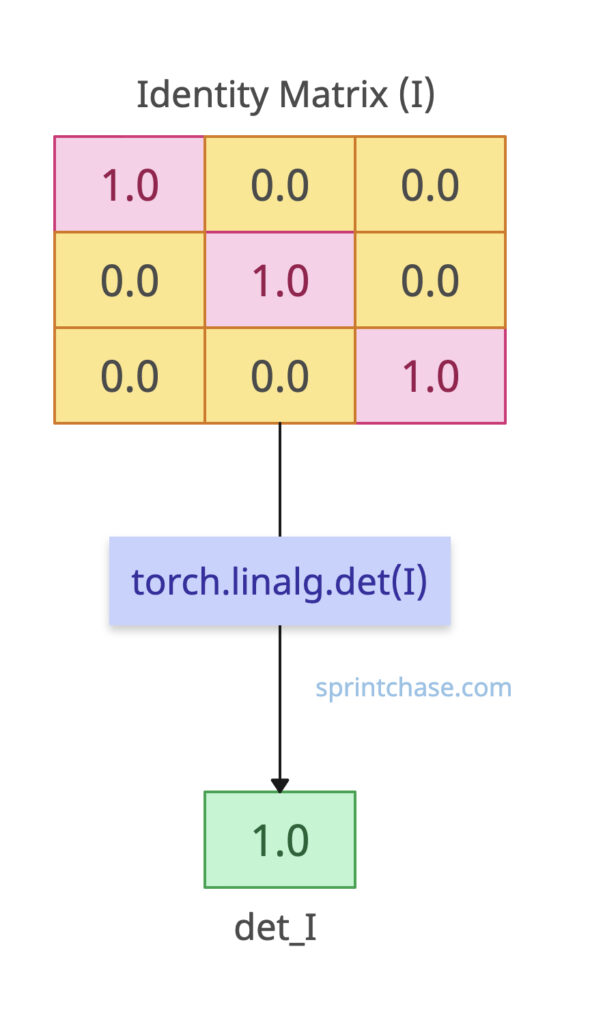 What if the input is an identity matrix? Well, determinant of the Identity matrix is always 1.
To create an identity matrix, use the torch.eye() method.
What if the input is an identity matrix? Well, determinant of the Identity matrix is always 1.
To create an identity matrix, use the torch.eye() method.
import torch I = torch.eye(3) det_I = torch.linalg.det(I) print(det_I) # Output: tensor(1.)
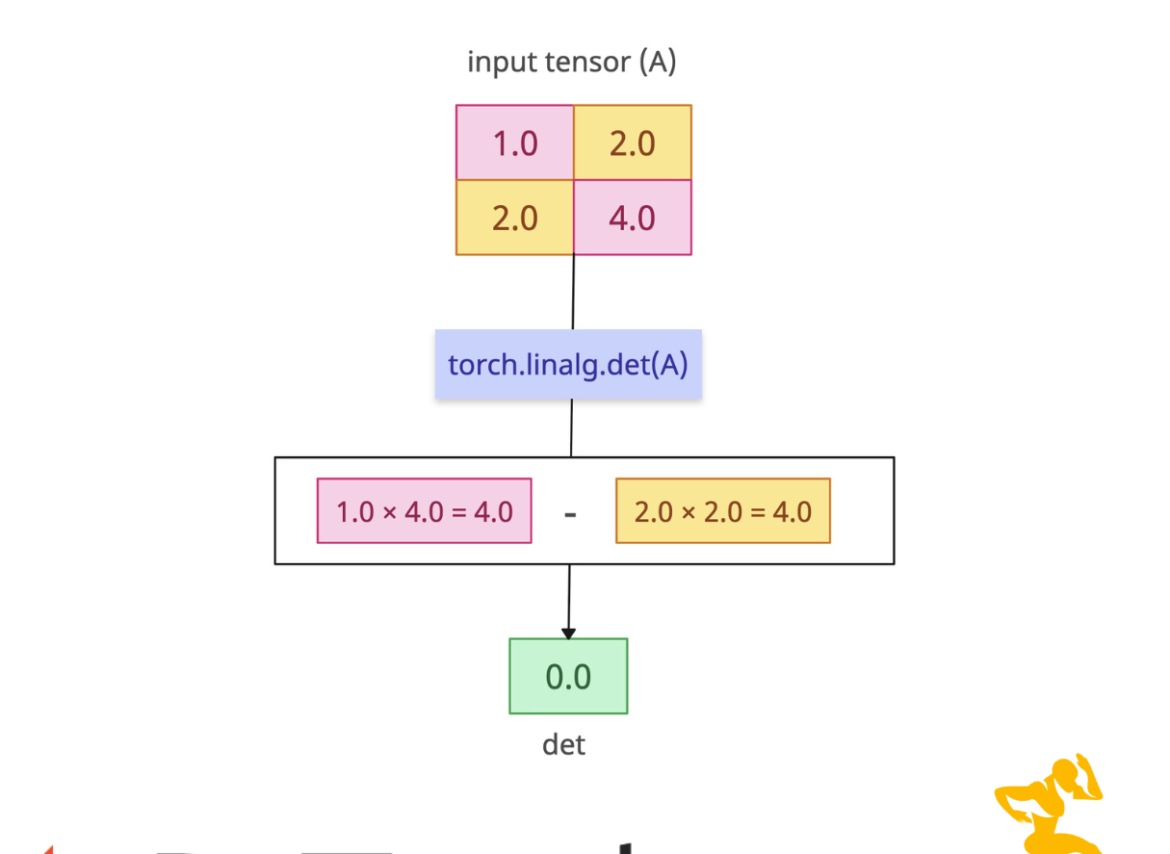
Singular Matrix (det=0)
If the input tensor is a singular matrix, the determinant is 0.
import torch singular = torch.tensor([[1., 2.], [2., 4.]]) det = torch.linalg.det(singular) # 1*4 - 2*2 = 0 print(det) # Output: tensor(0.)
Complex Matrix
If the input is a complex matrix, the output is also a complex tensor.import torch complex_mat = torch.tensor([[1+2j, 3j], [4., 5-1j]]) det = torch.linalg.det(complex_mat) # (1+2j)(5-1j) - (3j)(4) print(det) # Output: tensor(7.-3.j)
Empty matrix
If the input is an empty matrix, its determinant is 1.import torch empty_matrix = torch.empty(0, 0) det = torch.linalg.det(empty_matrix) print(det) # Output: tensor(1.)That’s all!