The torch.as_tensor() method converts an input data, such as Python lists, NumPy arrays, or Scalars, into a PyTorch tensor while optionally sharing memory with the input data.
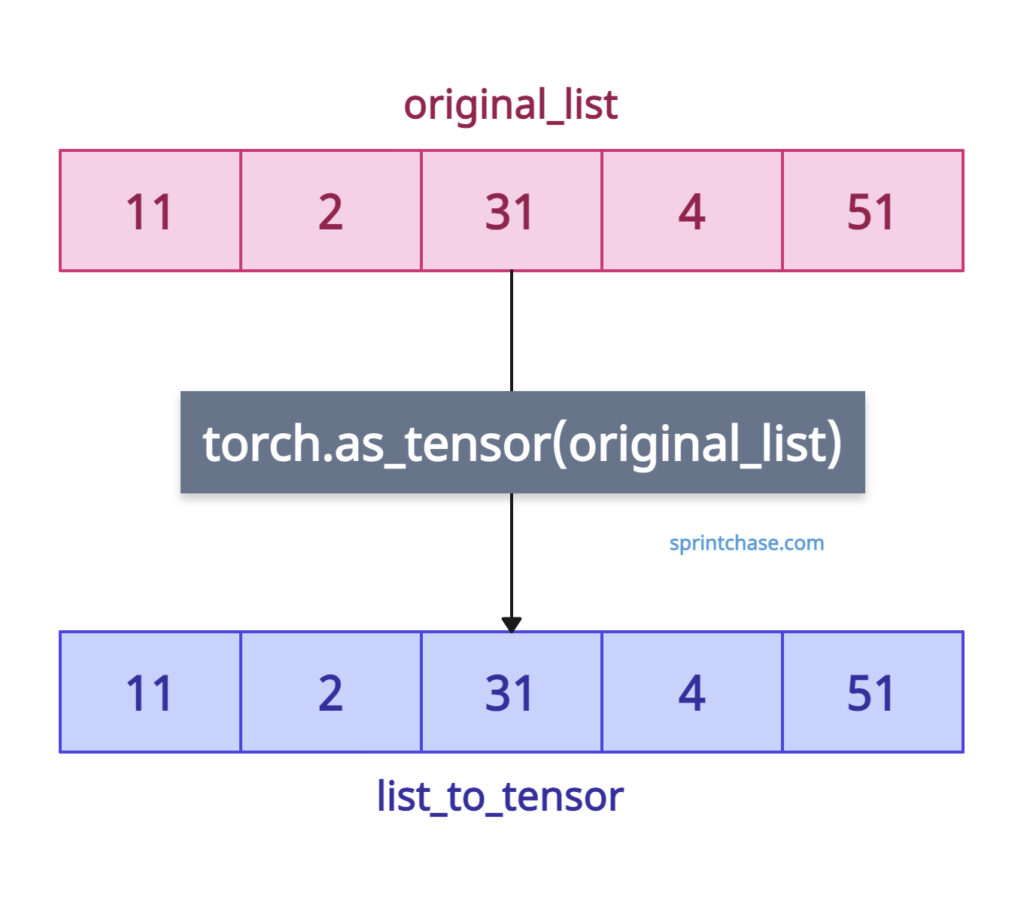 The above figure illustrates that the conversion from a list to a tensor is accomplished with a single method and a single argument.
The above figure illustrates that the conversion from a list to a tensor is accomplished with a single method and a single argument.
The main difference between torch.as_tensor() and torch.tensor() is that the .as_tensor() method prioritizes memory efficiency by sharing data when possible, making it ideal for integrating external data into PyTorch workflows.
Syntax
torch.as_tensor(data, dtype=None, device=None)
Arguments
| Name | Description |
| data (array_like) | It represents input data such as a tuple, a list, a numpy ndarray, a scalar, or other types. |
| dtype (torch.dtype, optional) | It is the desired data type of the returned tensor. |
| device (torch.device, optional) | It is the device used to create the tensor. By default, it is the device of data. However, you can specify an external device in this argument. |
Converting a list to a tensor
The most common use case is when your input is a list and you want to convert it to a PyTorch tensor.
Let’s define a simple 1D list and perform the conversion.
import torch original_list = [11, 2, 31, 4, 51] print(original_list) # Output: [11, 2, 31, 4, 51] print(type(original_list)) # Output: <class 'list'> list_to_tensor = torch.as_tensor(original_list) print(list_to_tensor) # Output: tensor([11, 2, 31, 4, 51]) print(type(list_to_tensor)) # Output: <class 'torch.Tensor'>
In the above code, with the help of as_tensor(), we easily converted the list to a tensor and verified the conversion using the built-in type() method.
Specifying a dtype
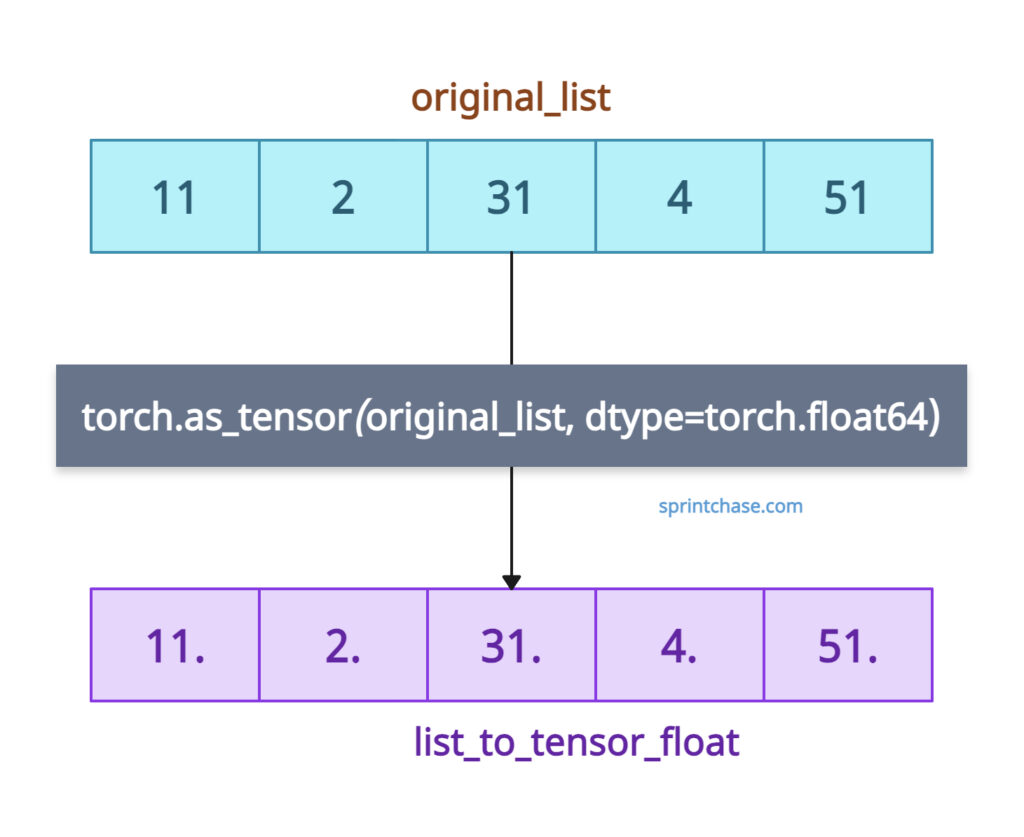
While converting data, we can specify the data type of the output tensor. Let’s take a look at the program below:
import torch original_list = [11, 2, 31, 4, 51] print(original_list) # Output: [11, 2, 31, 4, 51] print(type(original_list)) # Output: <class 'list'> list_to_tensor_float = torch.as_tensor(original_list, dtype=torch.float64) print(list_to_tensor_float) # Output: tensor([11., 2., 31., 4., 51.], dtype=torch.float64) print(type(list_to_tensor_float)) # Output: <class 'torch.Tensor'>
Specifying Device (CPU to GPU)
If a GPU is available, we can convert to Tensor on GPU using the device=’cuda’ argument.
import torch
# Input list
data = [11, 21, 19]
# Convert to tensor on GPU (if available)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
tensor = torch.as_tensor(data, device='cuda')
print(tensor)
else:
print("CUDA not available")
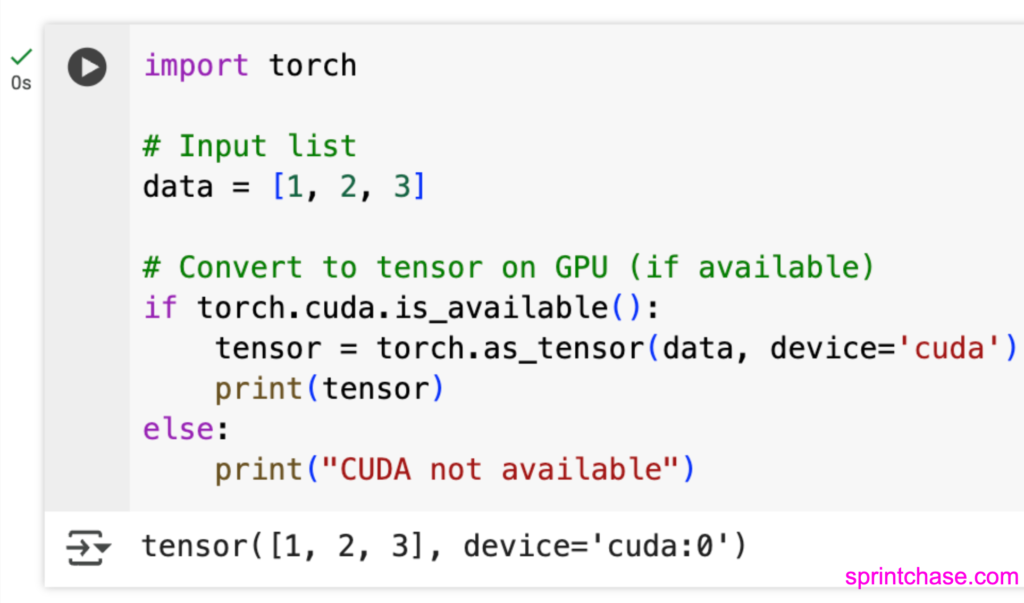
If you run the above code on a CPU, it will produce the “CUDA not available” output.
Converting a numpy array with memory sharing
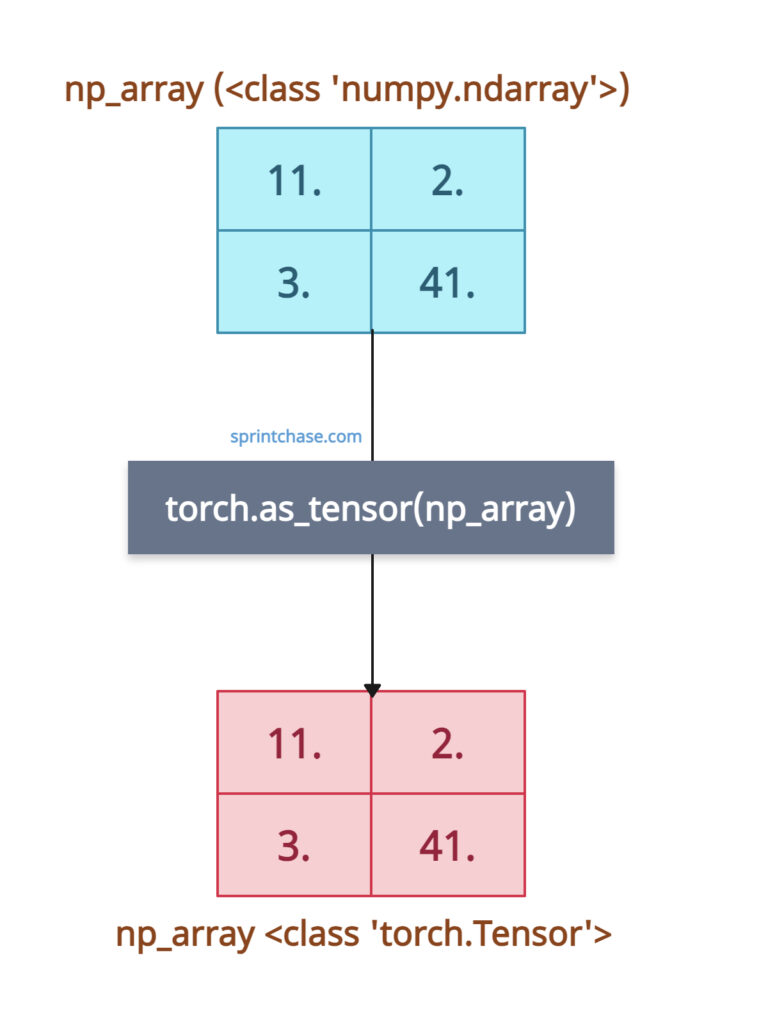
If an input is a numpy array, torch.as_tensor() shares the memory. Modifying the original numpy array affects the tensor, demonstrating zero-copy behavior.
import torch import numpy as np # Input NumPy array np_array = np.array([[11.0, 2.0], [3.0, 41.0]]) # Convert to tensor tensor = torch.as_tensor(np_array) print(tensor) # Output: tensor([[11., 2.], # [3., 41.]]) # Modify NumPy array np_array[0, 0] = 99.0 print(tensor) # Output: tensor([[99., 2.], # [3., 41.]])
Handling scalars
You can convert a single scalar value to a 0-dimensional tensor.
import torch # Input scalar scalar = 21 # Convert to tensor tensor = torch.as_tensor(scalar, dtype=torch.float32) print(tensor) # Output: tensor(21.)
Incompatible data types
What if we try to convert a list of strings to a tensor? In this case, it will throw ValueError: too many dimensions ‘str’.
PyTorch does not support strings as elements of tensors. Since strings are not numeric, it throws an error.
import torch
# Input list with non-numeric data
string_of_list = ["a", "b", "c"]
try:
tensor = torch.as_tensor(string_of_list)
except ValueError as e:
print(f"ValueError: {e}")
# ValueError: too many dimensions 'str'
To avoid this type of error, ensure that your input data contains integer or float values.
That’s all!





