The torch.initial_seed() method returns the initial seed for generating random numbers. The data type of the returned value is Python’s long type.

This method helps ensure reproducibility in experiments involving random operations, such as initializing model weights, shuffling datasets, or applying random transformations.
If you have used the torch.manual_seed() method to set the seed, it returns that seed or the default seed if none was explicitly set.
Syntax
torch.initial_seed()
This method accepts no arguments as it simply retrieves the seed value.
Retrieving the default seed
If in your program, no seed is explicitly set, the torch.initial_seed() method returns the default seed used by PyTorch.
import torch
# Get the initial seed
seed = torch.initial_seed()
print(f"Default initial seed: {seed}")
# Output: Default initial seed: 2071553450939988508
The output is a random seed that PyTorch sets.
Retrieving a custom seed
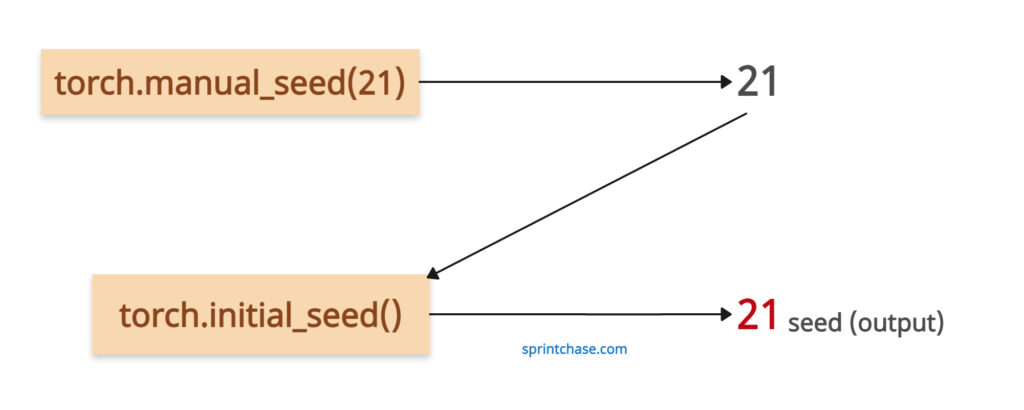
To set a custom seed, you can use the torch.manual_seed() method and then retrieve the seed using our method.
import torch
# Set a specific seed
torch.manual_seed(21)
# Retrieve the initial seed
seed = torch.initial_seed()
print(f"Initial seed after manual_seed: {seed}")
# Output: Initial seed after manual_seed: 21
Ensuring reproducibility across the program
To make experiments reproducible, set the seed and log it using this method.
import torch
# Set seed for reproducibility
torch.manual_seed(1234)
# Log the seed
seed = torch.initial_seed()
print(f"Experiment seed: {seed}")
# Output: Experiment seed: 1234
# Example random operation
tensor = torch.rand(3)
print(f"Random tensor: {tensor}")
# Output: Random tensor: tensor([0.0290, 0.4019, 0.2598])
That’s all!