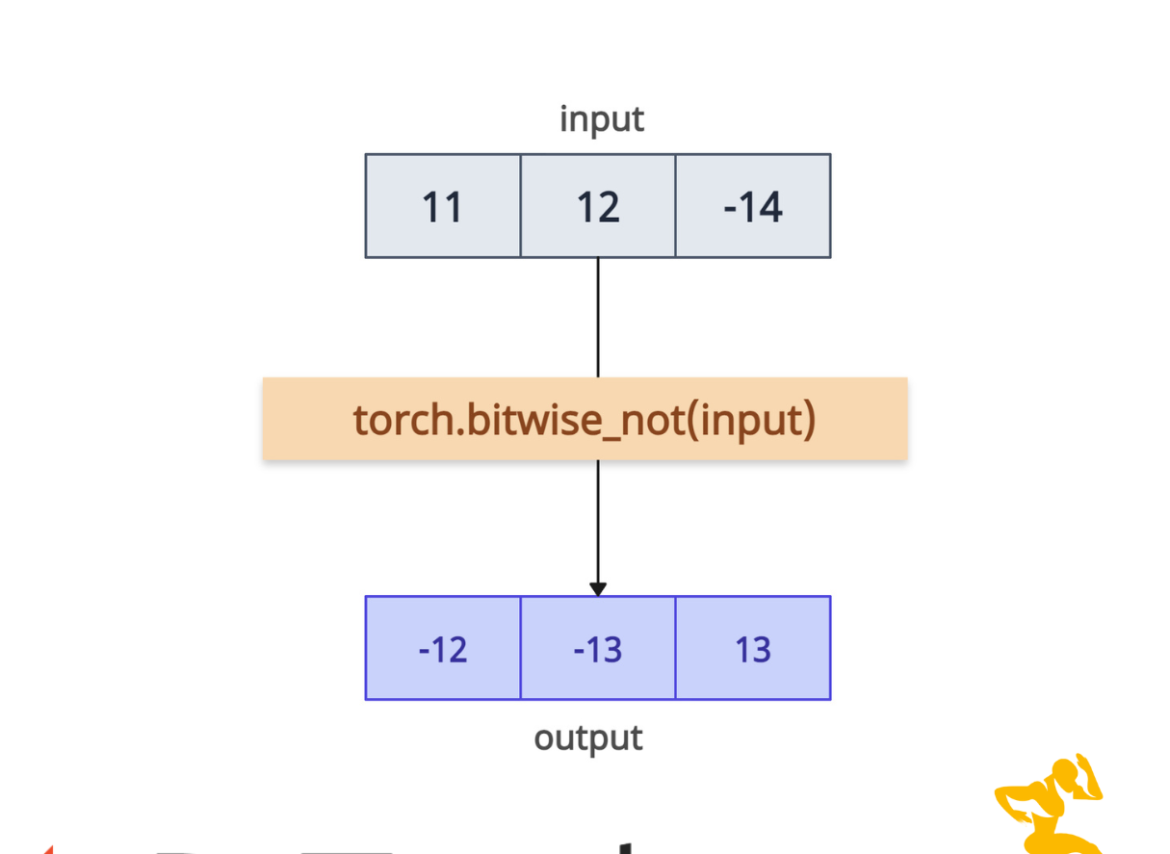
The torch.bitwise_not() method performs a bitwise NOT operation on the elements of an input tensor. A bitwise is a unary operation that inverts each bit in the operand. For example, 0 becomes 1 and 1 becomes 0.
Syntax
torch.bitwise_not(input, out=None)
Parameters
| Argument | Description |
| input (Tensor) | It represents a tensor that must be of type integer (torch.int8, torch.int16, torch.int32, torch.int64) or boolean type (torch.bool). |
| out (Tensor, optional) | By default, it is None. It is an output tensor to store the result. |
Bitwise NOT on Integer Tensors
It inverts all bits in the binary representation of each element.
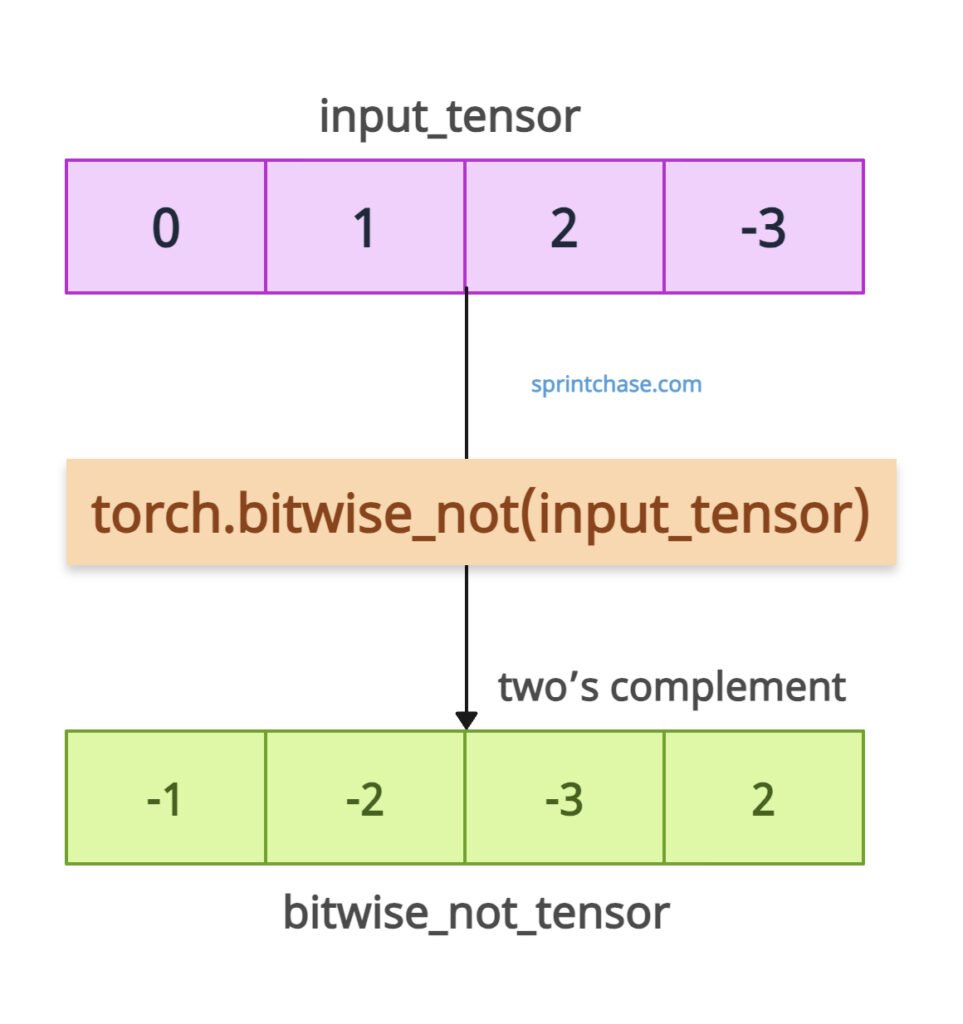
For signed integers, it uses two’s complement representation.
import torch # Create an integer tensor input_tensor = torch.tensor([0, 1, 2, -3], dtype=torch.int32) bitwise_not_tensor = torch.bitwise_not(input_tensor) print(input_tensor) print(bitwise_not_tensor) # Output: # tensor([ 0, 1, 2, -3], dtype=torch.int32) # tensor([-1, -2, -3, 2], dtype=torch.int32)Here is the explanation:
- 0 (binary: 00000000) becomes -1 (binary: 11111111, two’s complement).
- 1 (binary: 00000001) becomes -2 (binary: 11111110).
- 2 (binary: 00000010) becomes -3 (binary: 11111101).
- -3 (binary: 11111101) becomes 2 (binary: 00000010).
Boolean Tensors
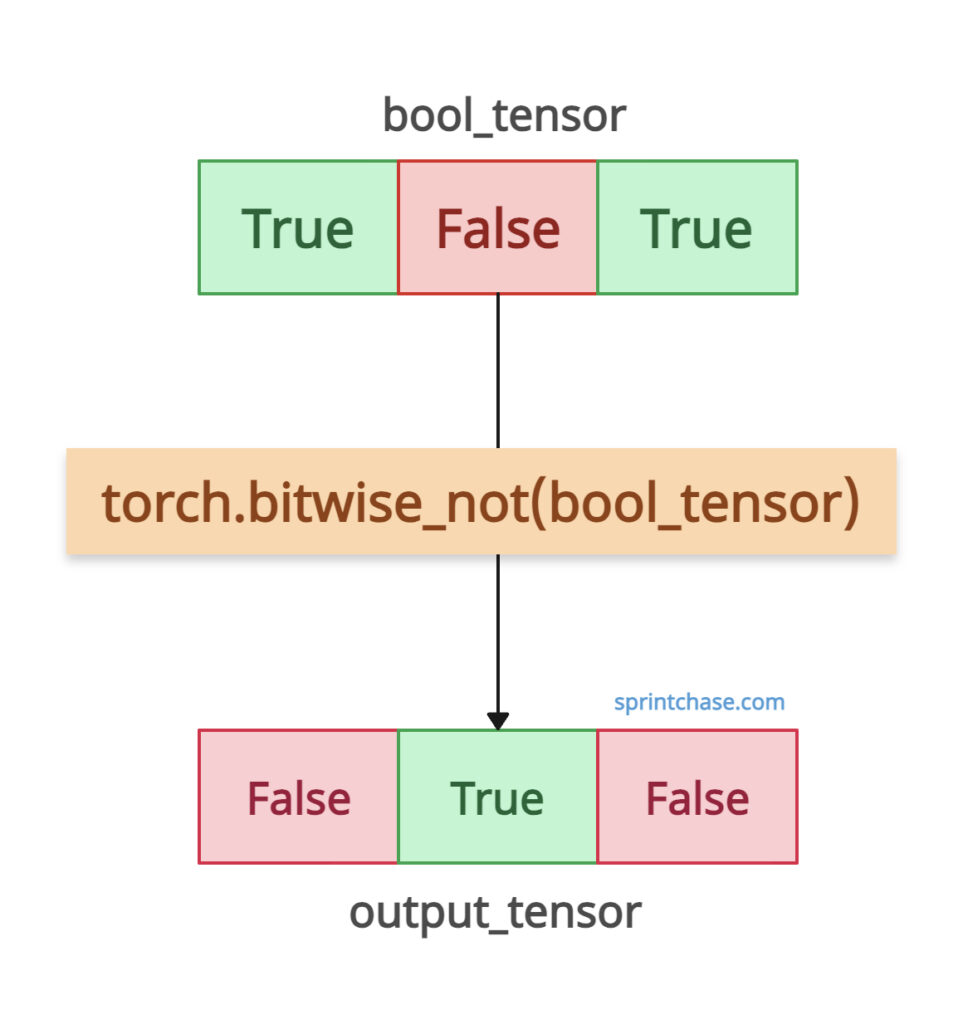
If your input is a boolean tensor (True or False), bitwise_not flips True to False and vice versa.
import torch # Create a boolean tensor bool_tensor = torch.tensor([True, False, True]) output_tensor = torch.bitwise_not(bool_tensor) print(bool_tensor) print(output_tensor) # Output: # tensor([ True, False, True]) # tensor([False, True, False])
Using the “out” Parameter
If you have a pre-allocated tensor, you can use the out parameter that allows us to store the result in a pre-allocated tensor.
import torch input_tensor = torch.tensor([5, -6], dtype=torch.int32) output_tensor = torch.empty_like(input_tensor) torch.bitwise_not(input_tensor, out=output_tensor) print(input_tensor) print(output_tensor) # Output: # tensor([ 5, -6], dtype=torch.int32) # tensor([-6, 5], dtype=torch.int32)
Unsupported Tensor Type
If you attempt to use the bitwise_not operator on a floating tensor, it will throw an error.
import torch
float_tensor = torch.tensor([1.0, 2.0])
try:
torch.bitwise_not(float_tensor)
except RuntimeError as e:
print("Error:", e)
# Output: Error: "bitwise_not_cpu" not implemented for 'Float'
That’s all!